Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2019; 25(31): 4383-4404
Published online Aug 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i31.4383
Published online Aug 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i31.4383
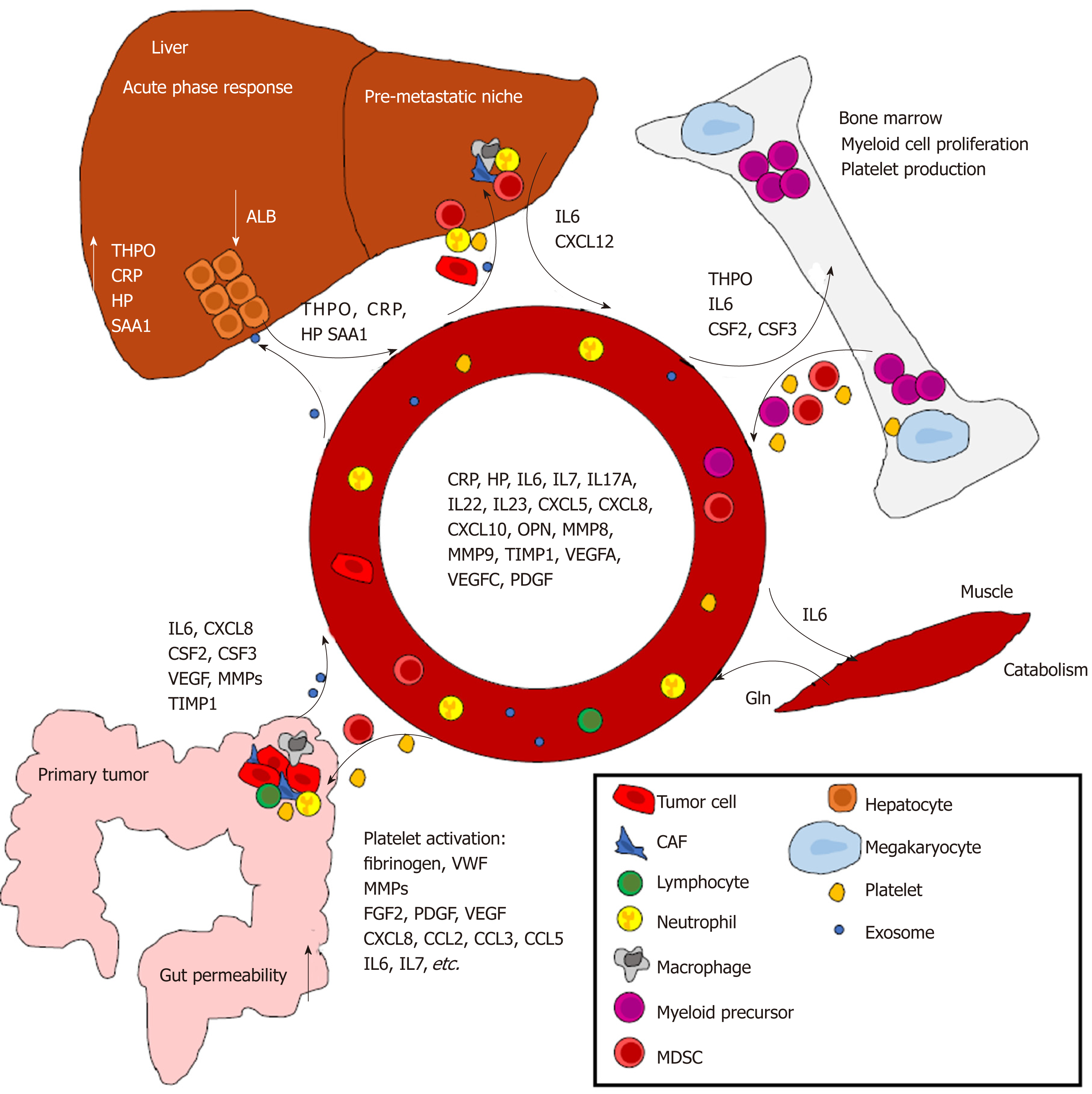
Figure 2 Overview of the effects of systemic inflammation in colorectal cancer.
The illustration portrays some of the molecules and phenomena considered important in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer associated systemic inflammation. Some markers showing increased circulating concentrations in colorectal cancer patients are listed in the center. ALB: Albumin; CCL: C-C motif chemokine ligand; CXCL: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand; CRP: C-reactive protein; CSF: Colony stimulating factor; FGF2: Fibroblast growth factor 2; Gln: Glutamine; HP: Haptoglobin; IL: Interleukin; MMP: Matrix metallopeptidase; OPN: Osteopontin; PDGF: Platelet derived growth factor; SAA1: Serum amyloid A1; THPO: Thrombopoietin; TIMP1: TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 1; VEGFA: Vascular endothelial growth factor A; VEGFC: Vascular endothelial growth factor C; vWF: von Willebrand factor
- Citation: Tuomisto AE, Mäkinen MJ, Väyrynen JP. Systemic inflammation in colorectal cancer: Underlying factors, effects, and prognostic significance. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(31): 4383-4404
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i31/4383.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i31.4383