Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2019; 25(29): 3956-3971
Published online Aug 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i29.3956
Published online Aug 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i29.3956
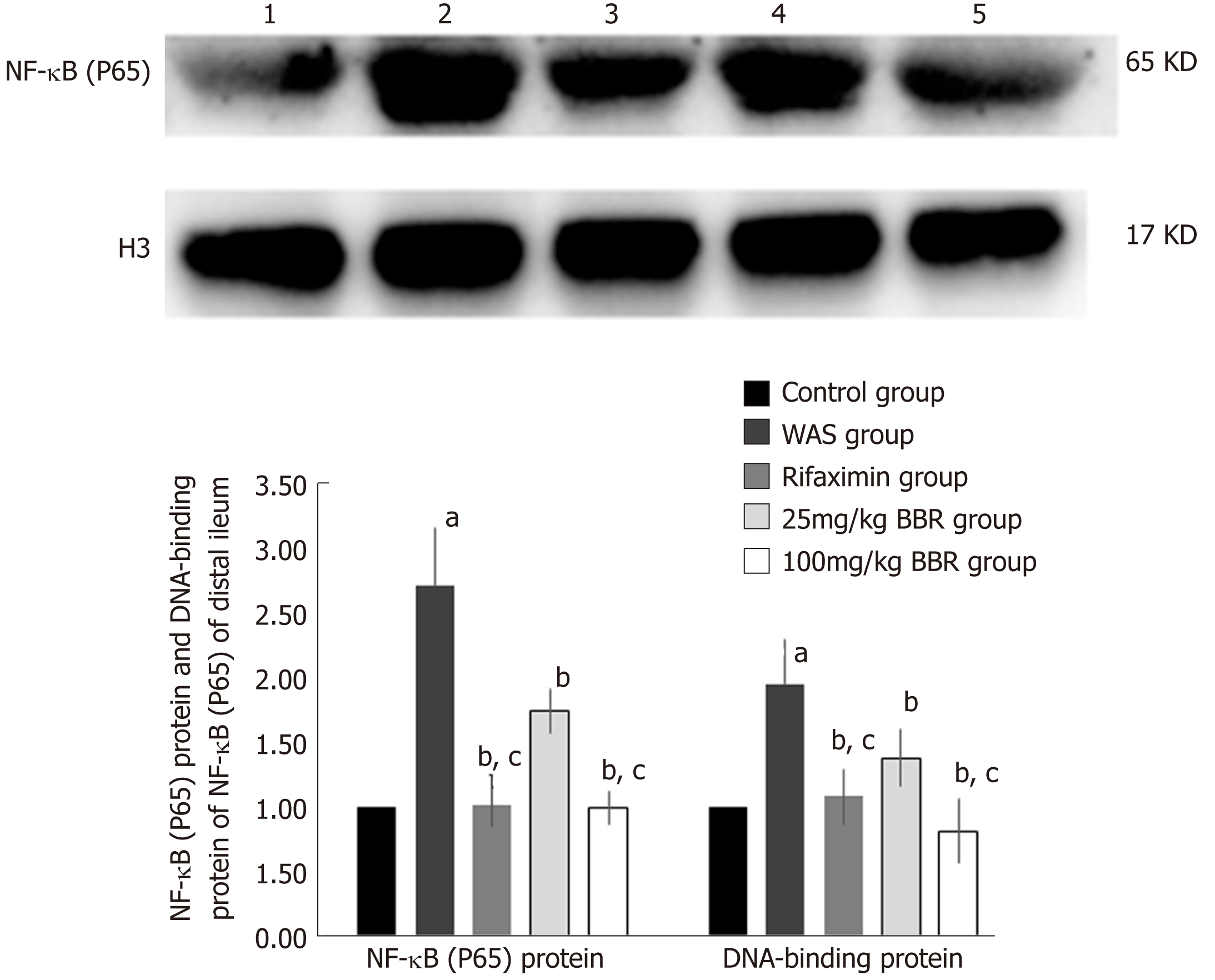
Figure 3 Effects of berberine on NF-κB (P65) protein and NF-κB (P65) DNA-binding protein expression.
Expression of NF-κB (P65) protein and DNA-binding protein of NF-κB in 1: Control group; 2: Water avoidance stress (WAS) group; 3: Rifaximin group; 4: 25 mg/kg berberine (BBR) group; 5: 100 mg/kg BBR group. Letters a, b, and c: P < 0.05 compared with those in the control group, WAS group, and 25 mg/kg BBR group, respectively. WAS: Water avoidance stress; BBR: Berberine.
- Citation: Yu ZC, Cen YX, Wu BH, Wei C, Xiong F, Li DF, Liu TT, Luo MH, Guo LL, Li YX, Wang LS, Wang JY, Yao J. Berberine prevents stress-induced gut inflammation and visceral hypersensitivity and reduces intestinal motility in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(29): 3956-3971
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i29/3956.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i29.3956