Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2019; 25(29): 3956-3971
Published online Aug 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i29.3956
Published online Aug 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i29.3956
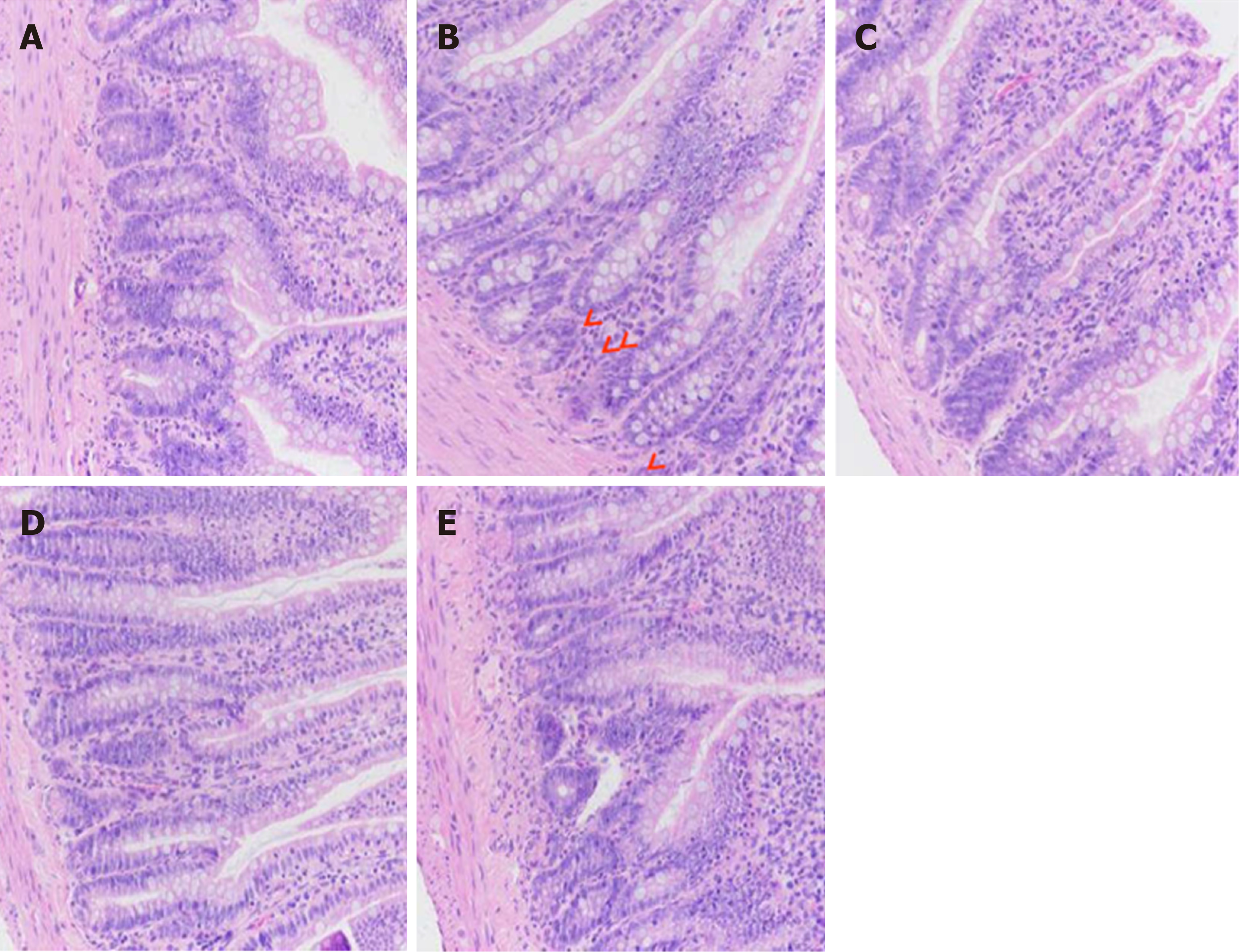
Figure 2 Effects of berberine on histological score of the distal intestine in rats (×200).
A: Control group; B: Water avoidance stress group; C: Rifaximin group; D: 25 mg/kg berberine (BBR) group; E: 100 mg/kg BBR group (the labeled cells are neutrophils). Compared with the control group (A), rats in the water avoidance stress (WAS) group (B) showed low-grade intestinal inflammatory reaction. Microscopically, the tissues of the terminal ileum were intact, the mucosal structure and epithelium were intact, and the crypt was intact. Compared with the WAS group, after treatment with rifaximin (C), 25 mg/kg BBR (D), or 100 mg/kg BBR (E), the tissues of the terminal ileum of rats were intact, the mucosal structure and epithelium were intact, the crypt was intact, and no obvious neutrophil infiltration was observed. WAS: Water avoidance stress; BBR: Berberine.
- Citation: Yu ZC, Cen YX, Wu BH, Wei C, Xiong F, Li DF, Liu TT, Luo MH, Guo LL, Li YX, Wang LS, Wang JY, Yao J. Berberine prevents stress-induced gut inflammation and visceral hypersensitivity and reduces intestinal motility in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(29): 3956-3971
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i29/3956.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i29.3956