Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2019; 25(29): 3941-3955
Published online Aug 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i29.3941
Published online Aug 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i29.3941
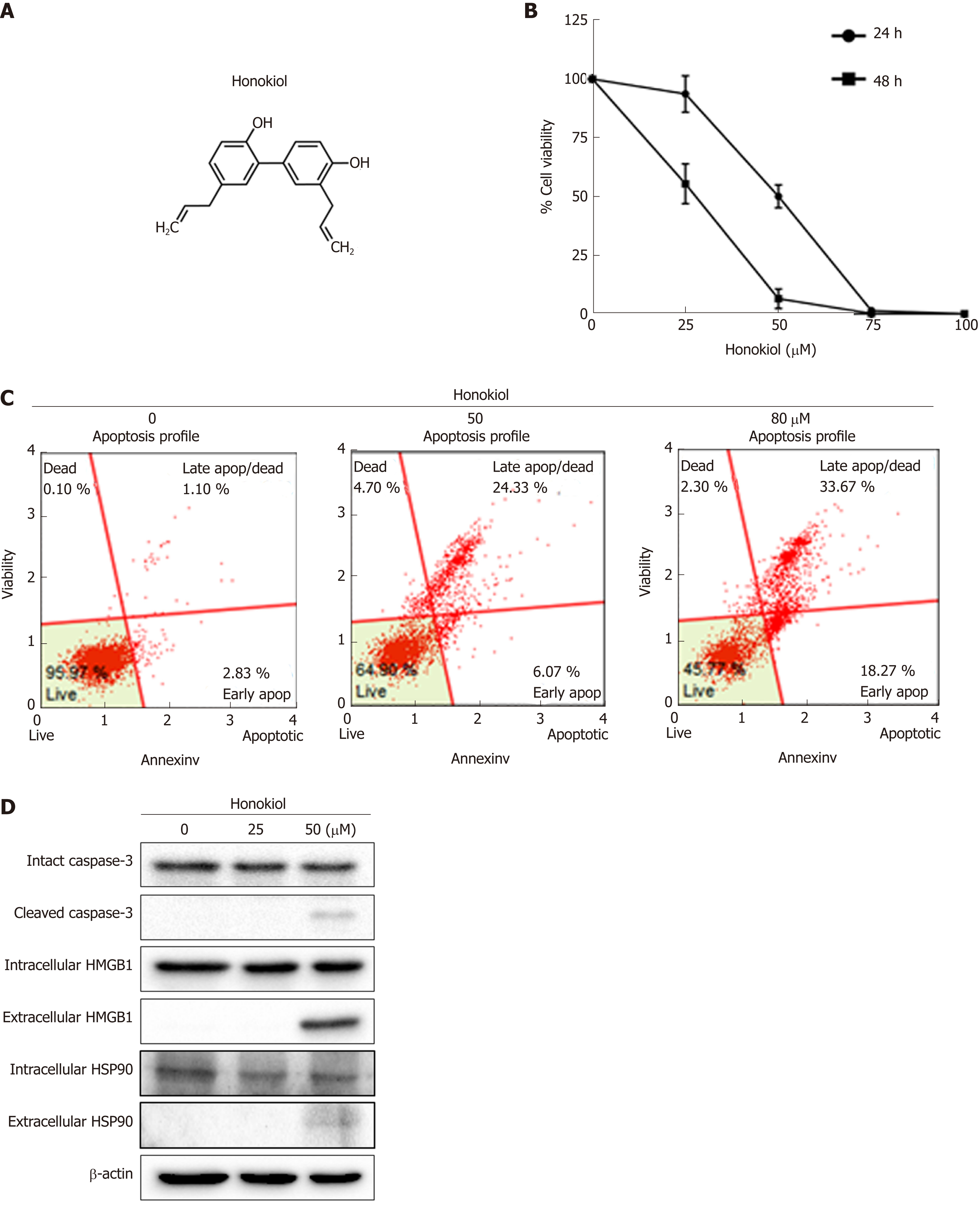
Figure 1 Honokiol induced cholangiocarcinoma cell apoptosis and cause of Damage- associated molecular pattern secretion.
A: Chemical structure of honokiol; B: KKU-213L5 cells were treated with various concentrations of honokiol. After 24 and 48 h, cell viability was accessed using MTT assay. Negative control was cells treated with dimethyl sulfoxide and all groups were normalised with the control group. Results were presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments; C: Treated KKU-213L5 cells were analyzed using Muse™ Cell Analyser with annexin V/PI staining. Annexin V versus propidium iodide from the gated cells revealed cell populations as live, early apoptotic, late apoptotic/dead and dead; D: Protein samples and conditioned medium were collected and analysed using Western blot. HMGB1: High mobility group box1; HSP: Heat shock protein.
- Citation: Jiraviriyakul A, Songjang W, Kaewthet P, Tanawatkitichai P, Bayan P, Pongcharoen S. Honokiol-enhanced cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity against cholangiocarcinoma cells mediated by dendritic cells pulsed with damage-associated molecular patterns. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(29): 3941-3955
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i29/3941.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i29.3941