Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2019; 25(27): 3590-3606
Published online Jul 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i27.3590
Published online Jul 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i27.3590
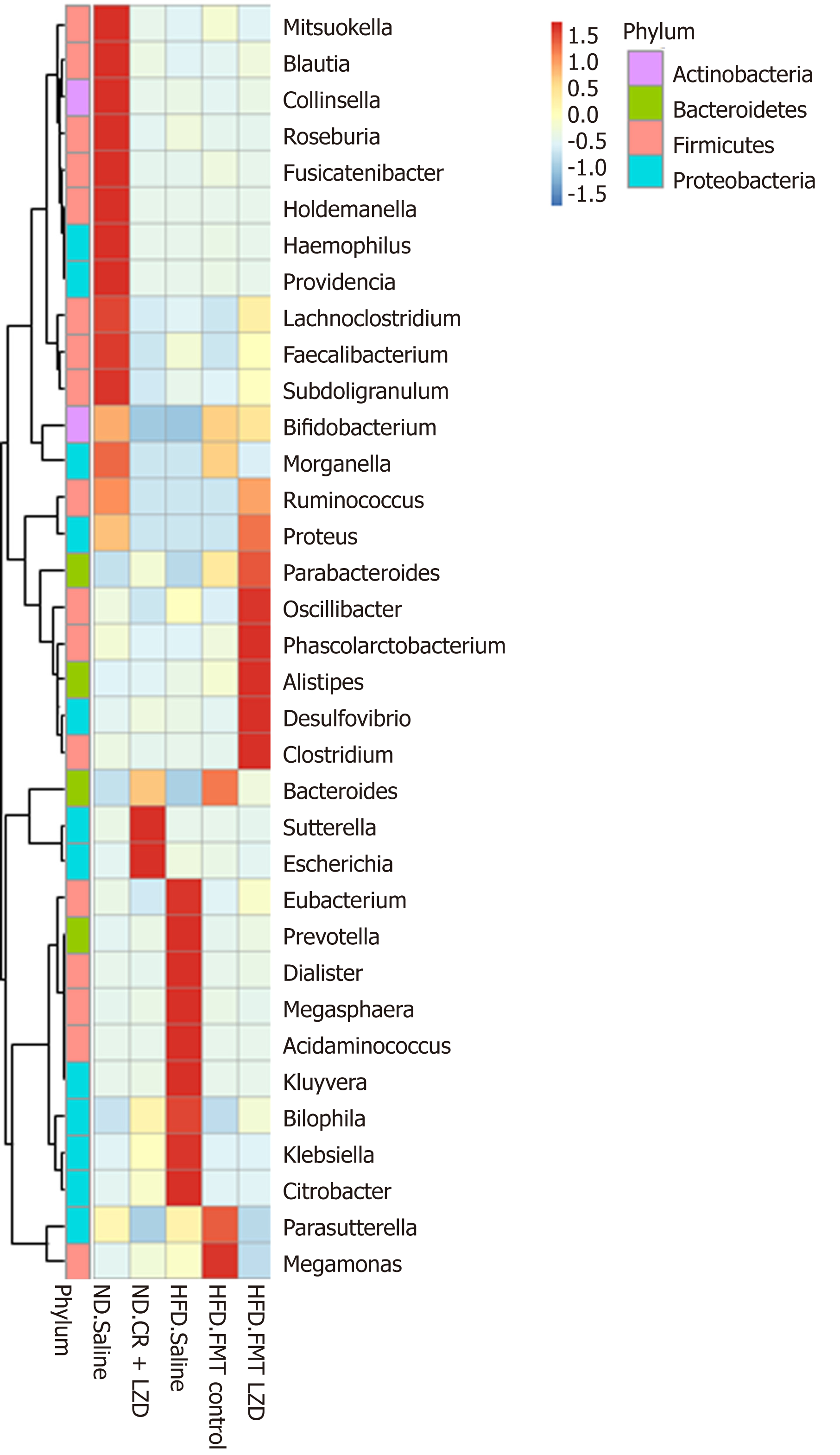
Figure 7 Relative abundance of gut microbiota at the genus level.
ND. Saline: Mice fed normal diet (ND) and given saline gavage; ND. CR + LZD: Mice fed ND and given caloric restriction (CR) and Lingguizhigan decoction (LZD) treatment; HFD. Saline: Mice fed high-fat diet (HFD) and given saline gavage; HFD. FMT control: Mice fed HFD and given fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) from ND. Saline mice; HFD. FMT CR + LZD: Mice fed HFD and given FMT from ND. CR + LZD mice; ND: Normal diet; LZD: Lingguizhigan decoction; HFD: High-fat diet; FMT: Fecal microbiota transplantation; CR: Caloric restriction.
- Citation: Liu MT, Huang YJ, Zhang TY, Tan LB, Lu XF, Qin J. Lingguizhugan decoction attenuates diet-induced obesity and hepatosteatosis via gut microbiota. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(27): 3590-3606
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i27/3590.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i27.3590