Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2019; 25(27): 3590-3606
Published online Jul 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i27.3590
Published online Jul 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i27.3590
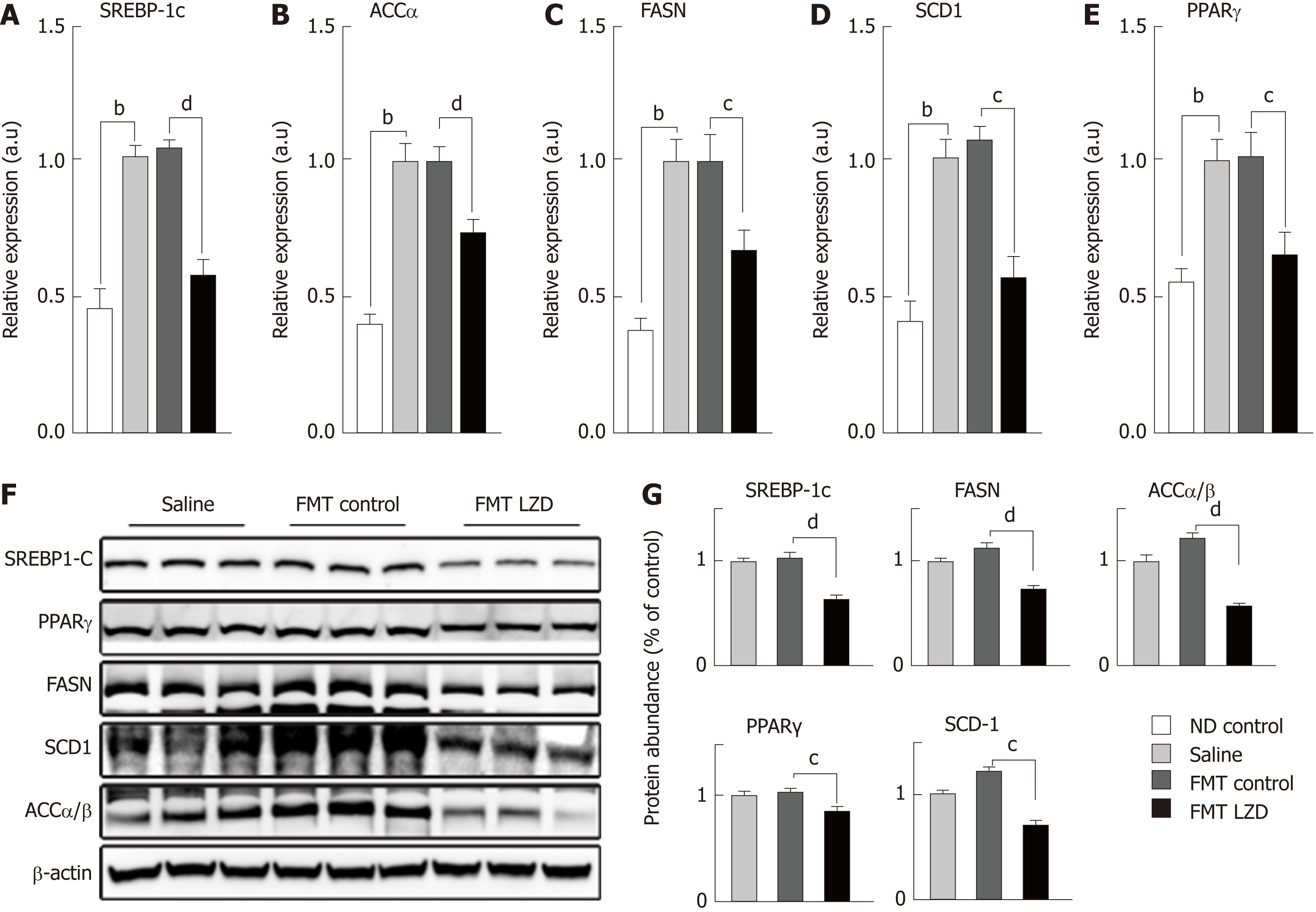
Figure 4 Fecal microbiota transplantation from caloric restriction and Lingguizhugan decoction-treated normal diet-fed mice into high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice reduces expression level and protein abundance of lipogenic genes.
Total RNA was isolated from liver samples from saline-treated mice (pink), fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) control mice (green), and FMT Lingguizhigan decoction (LZD)-treated mice (blue). A-E: Gene expression was analyzed and normalized to 36B4 expression in the same sample; n = 10 per group; F: Representative blot of liver samples; G: Protein abundance of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ, fatty acid synthase, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1, and acetyl-CoA carboxylase α/β was quantified and normalized to β-actin levels in the same lysate; n = 9 per group. Data were evaluated for statistical significance by one-way ANOVA and are represented as follows: aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs normal diet control with Saline; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 FMT LZD vs FMT control. ND: Normal diet; LZD: Lingguizhigan decoction; HFD: High-fat diet; FMT: Fecal microbiota transplantation; SREBP: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein; ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; FASN: Fatty acid synthase; SCD: Stearoyl-CoA desaturase; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor.
- Citation: Liu MT, Huang YJ, Zhang TY, Tan LB, Lu XF, Qin J. Lingguizhugan decoction attenuates diet-induced obesity and hepatosteatosis via gut microbiota. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(27): 3590-3606
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i27/3590.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i27.3590