Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2019; 25(27): 3503-3526
Published online Jul 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i27.3503
Published online Jul 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i27.3503
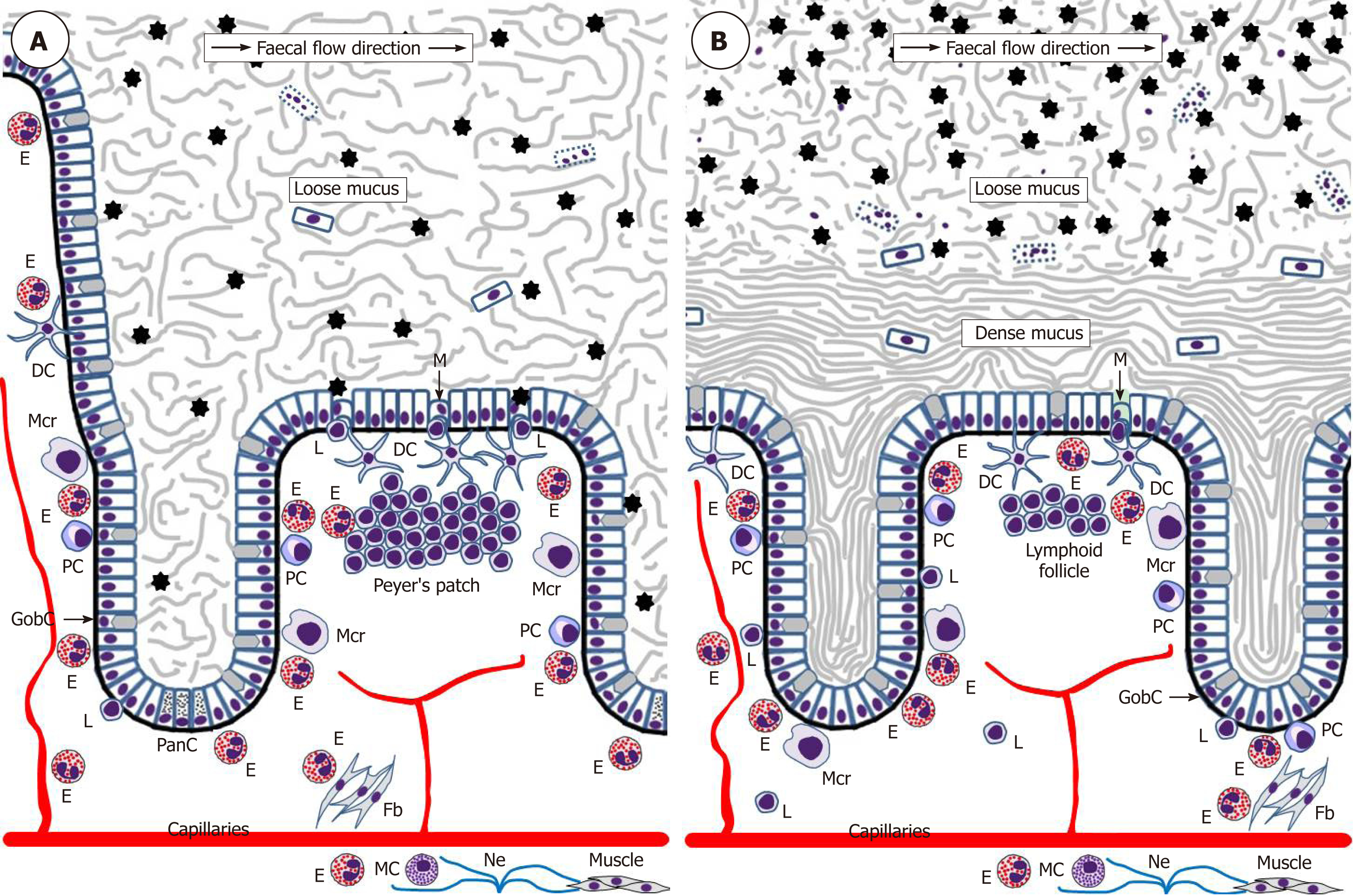
Figure 2 Schematic representation of eosinophil interactions with other cells and tissues in the small intestine (A) and colon (B).
Black asterisks indicate gut microbiota. Although one M-cell is shown in the colon, little is known about the presence of M-cells in healthy human colon.DC: Dendritic lells; E: Eosinophils; Fb: Fibroblasts; GobC: Goblet cells; L: Lymphocytes; M: M-cells; Mcr: Macrophages; Ne: Nerves; PanC: Paneth cells; PC: Plasma cells.
- Citation: Loktionov A. Eosinophils in the gastrointestinal tract and their role in the pathogenesis of major colorectal disorders. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(27): 3503-3526
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i27/3503.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i27.3503