Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2019; 25(25): 3242-3255
Published online Jul 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3242
Published online Jul 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3242
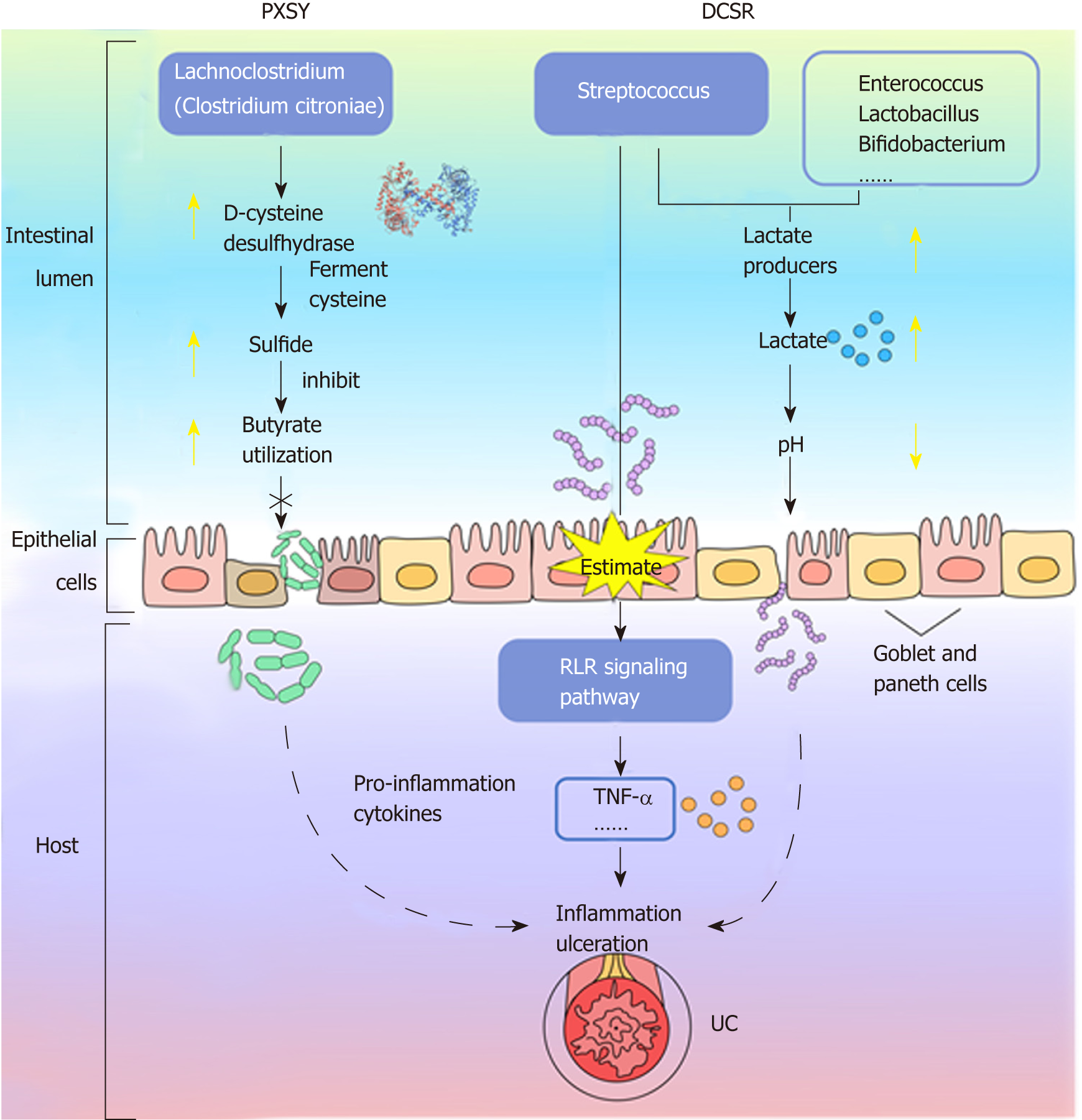
Figure 6 The probable contribution of the gut microbiota to the pathological mechanism of Da-Chang-Shi-Re and Pi-Xu-Shi-Yun syndromes.
Da-Chang-Shi-Re and Pi-Xu-Shi-Yun syndromes might have different pathological mechanisms, which are based on the differential microbiota between these two syndromes. UC: Ulcerative colitis; DCSR: Da-Chang-Shi-Re syndrome; PXSY: Pi-Xu-Shi-Yun syndrome; RLR: RIG-I-like receptor.
- Citation: Zhang YL, Cai LT, Qi JY, Lin YZ, Dai YC, Jiao N, Chen YL, Zheng L, Wang BB, Zhu LX, Tang ZP, Zhu RX. Gut microbiota contributes to the distinction between two traditional Chinese medicine syndromes of ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(25): 3242-3255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i25/3242.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3242