Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2019; 25(25): 3242-3255
Published online Jul 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3242
Published online Jul 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3242
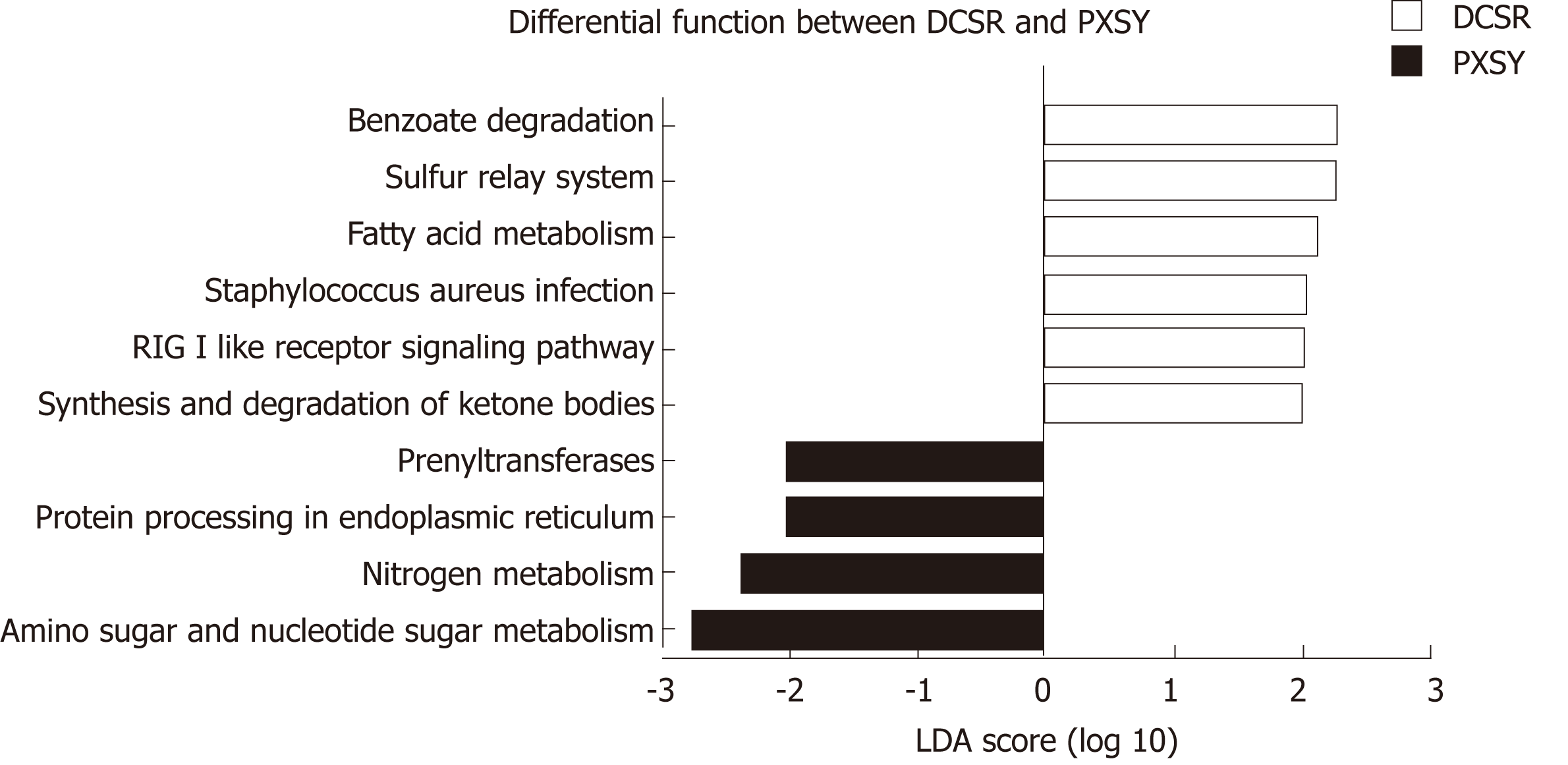
Figure 5 Functional pathways of gut microbiomes in the Pi-Xu-Shi-Yun and Da-Chang-Shi-Re groups.
Microbial functions were predicted and categorized into KEGG pathways using Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States. Linear discriminant analysis effect size was carried out to detect inner function differentials among groups. Significantly differential functions between Pi-Xu-Shi-Yun syndrome (yellow) and Da-Chang-Shi-Re syndrome (pink) are shown (LDA score > 2.0). DCSR: Da-Chang-Shi-Re syndrome; PXSY: Pi-Xu-Shi-Yun syndrome.
- Citation: Zhang YL, Cai LT, Qi JY, Lin YZ, Dai YC, Jiao N, Chen YL, Zheng L, Wang BB, Zhu LX, Tang ZP, Zhu RX. Gut microbiota contributes to the distinction between two traditional Chinese medicine syndromes of ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(25): 3242-3255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i25/3242.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3242