Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2019; 25(20): 2450-2462
Published online May 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i20.2450
Published online May 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i20.2450
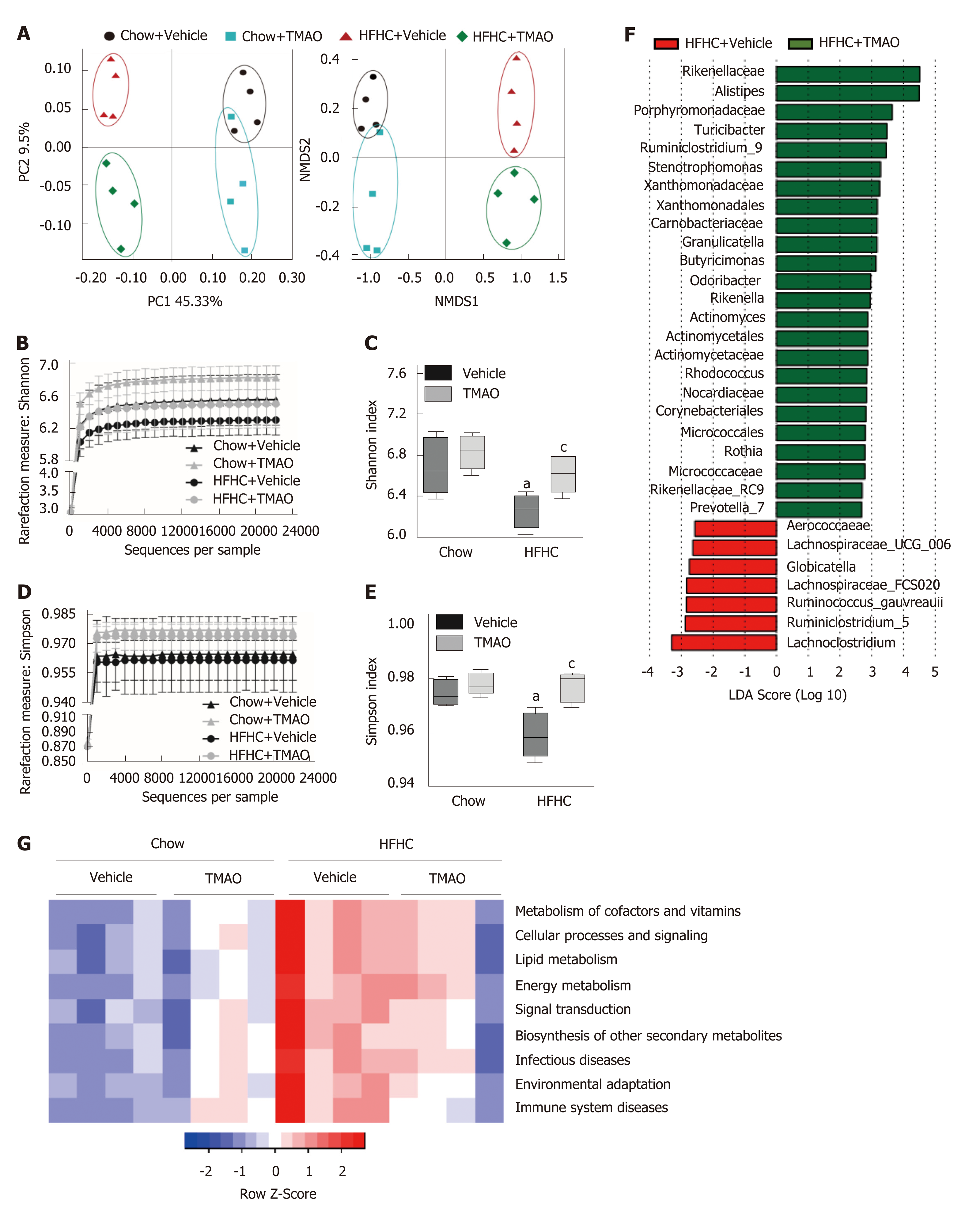
Figure 6 Diversity of gut microbiota is restored by trimethylamine N-oxide treatment in rats fed a high-fat high-cholesterol diet.
A: The beta diversity of the gut microbiota (n = 4); B: The rarefaction curve of the Shannon measurement (n = 4); C: Index bar of the Shannon measurement (n = 4); D: The rarefaction curve of the Simpson measurement (n = 4); E: Index bar of the Simpson measurement (n = 4); F: Linear discriminant analysis coupled with effect size measurements analysis (n = 4); G: Prediction of the functional genes in the sampled bacterial community using phylogenetic investigation of communities by reconstruction of unobserved states (n = 4). aP < 0.05, vs rats fed a chow diet; bP < 0.01, vs rats fed a chow diet; cP < 0.05, vs rats fed a high-fat high-cholesterol diet; dP < 0.01, vs rats fed a high-fat high-cholesterol diet. TMAO: Trimethylamine N-oxide; HFHC: High-fat high-cholesterol.
- Citation: Zhao ZH, Xin FZ, Zhou D, Xue YQ, Liu XL, Yang RX, Pan Q, Fan JG. Trimethylamine N-oxide attenuates high-fat high-cholesterol diet-induced steatohepatitis by reducing hepatic cholesterol overload in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(20): 2450-2462
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i20/2450.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i20.2450