Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2019; 25(19): 2315-2326
Published online May 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i19.2315
Published online May 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i19.2315
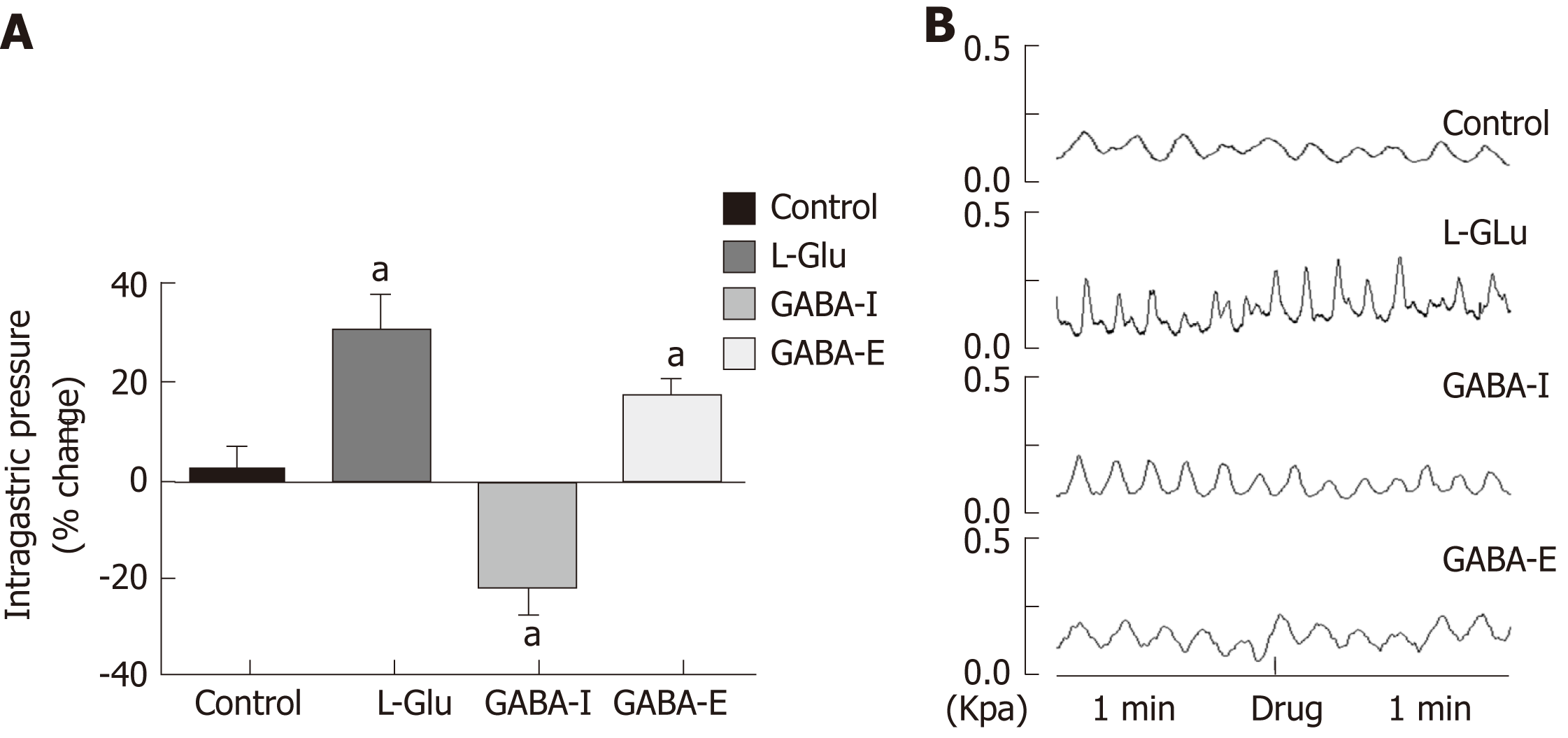
Figure 5 Gastric motility changes after dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve microinjection of different amino acids.
A: Percentage change of gastric motility after microinjection of artificial cerebrospinal fluid, glutamic acid, or γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) into dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve (DMV) (GABA-I is the inhibitory effect group, and GABA-E is the excitatory effect group); aP < 0.05 compared with the control group; B: Waveform of gastric movement changes after microinjection of artificial cerebrospinal fluid, glutamic acid, and GABA into the DMV. GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid; DMV: Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve; L-Glu: Glutamate.
- Citation: Lu MJ, Yu Z, He Y, Yin Y, Xu B. Electroacupuncture at ST36 modulates gastric motility via vagovagal and sympathetic reflexes in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(19): 2315-2326
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i19/2315.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i19.2315