Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2019; 25(18): 2204-2216
Published online May 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i18.2204
Published online May 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i18.2204
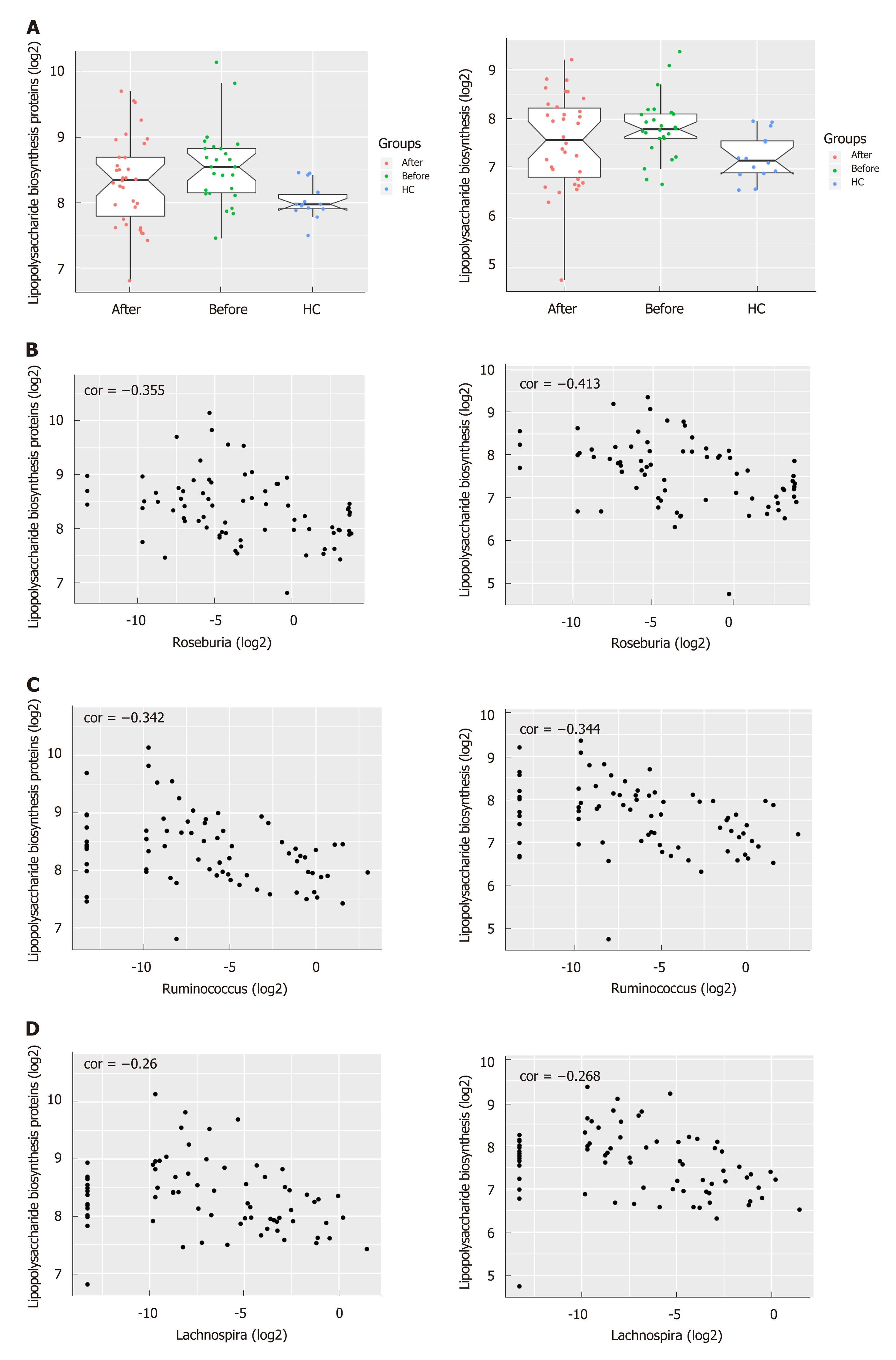
Figure 4 The predicted functional module involving pro-inflammatory pathways altered in Crohn’s disease compared to healthy controls.
A: Pathways including Lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis proteins and Lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis predicted to show significant different abundances among before, after and healthy controls group according to Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genome pathway analysis. The Crohn’s disease-depleted genera including Roseburia, Ruminococcus and Lachnospira were negatively correlated with Lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis proteins (P = 0.001 for Roseburia, P = 0.002 for Ruminococcus and P = 0.025 for Lachnospira) and Lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis (P = 0.0002 for Roseburia, P = 0.002 for Ruminococcus and P = 0.021 for Lachnospira). B: Roseburia; C: Ruminococcus; D: Lachnospira.
- Citation: He C, Wang H, Liao WD, Peng C, Shu X, Zhu X, Zhu ZH. Characteristics of mucosa-associated gut microbiota during treatment in Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(18): 2204-2216
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i18/2204.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i18.2204