Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2019; 25(18): 2188-2203
Published online May 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i18.2188
Published online May 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i18.2188
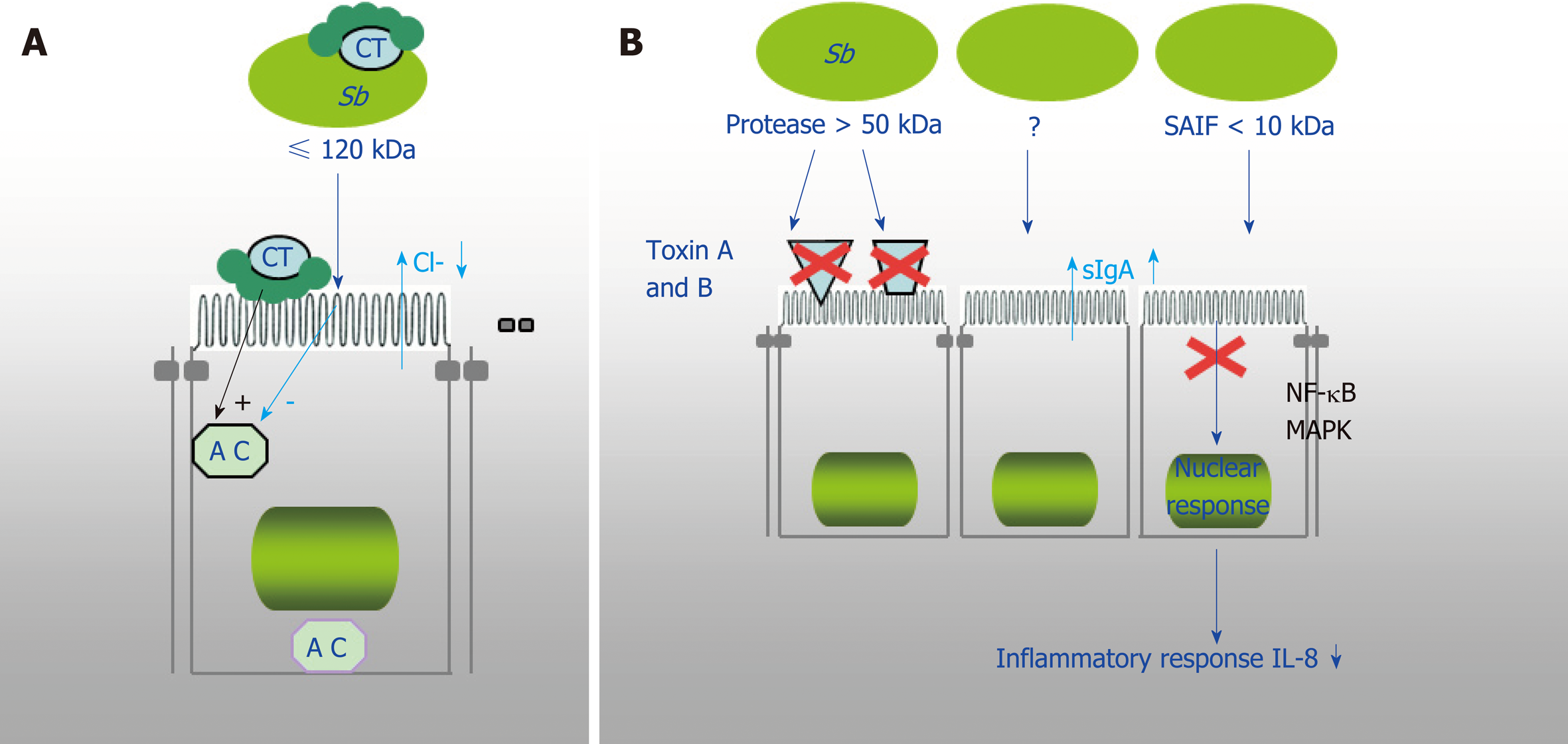
Figure 3 Demonstrated mechanism of Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 action against bacterial toxins.
A: Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 (S. b) produces a 120 kDa protein that inhibits adenylate cyclase and cholera toxin (CT)-induced chloride secretion. S. boulardii CNCM I-745 can also bind to CT; B: S. boulardii CNCM I-745 secretes a protease (> 54kDa) that lyses C. difficile toxins A and B and their receptors and a protein (< 10 kDa) that inhibits the signaling pathways involved in interleukin 8 synthesis. AC: Adenylate cyclase; CT: Cholera toxin; Sb: Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745; IL-8: Interleukin 8.
- Citation: Czerucka D, Rampal P. Diversity of Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 mechanisms of action against intestinal infections. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(18): 2188-2203
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i18/2188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i18.2188