Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2019; 25(17): 2071-2085
Published online May 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i17.2071
Published online May 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i17.2071
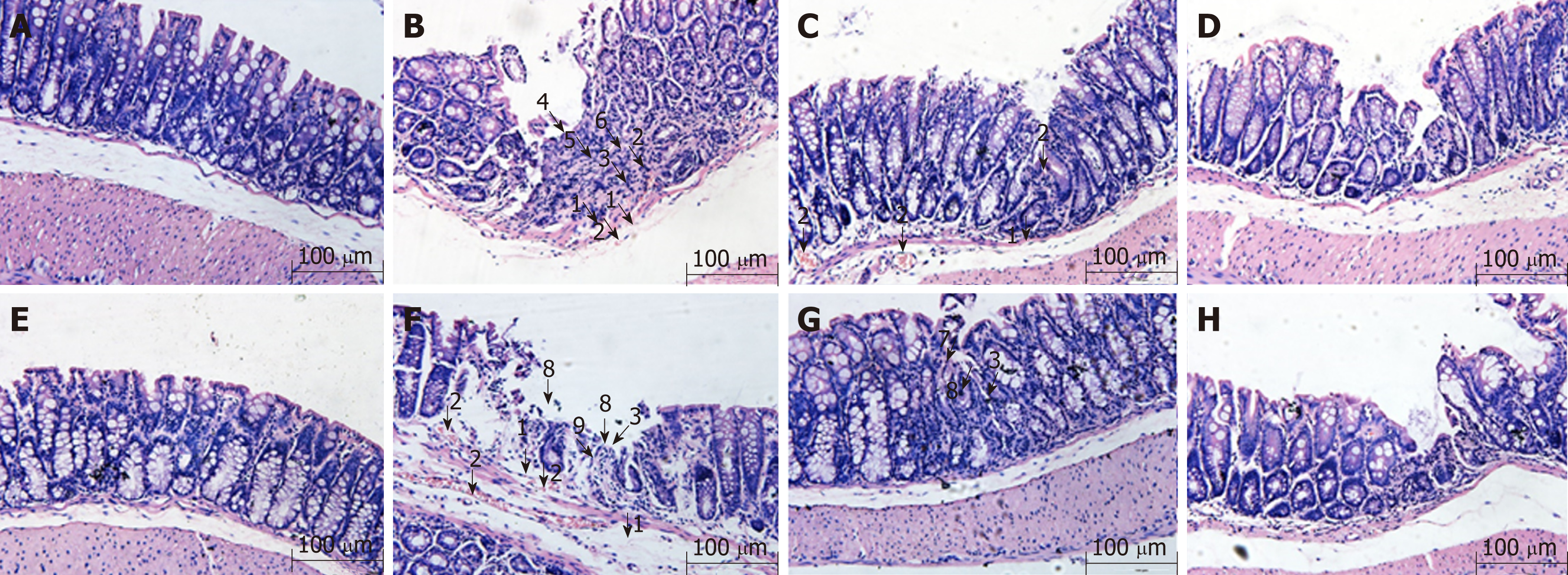
Figure 1 Histological observation of intestinal epithelial tissues across groups (magnification, ×100).
A: Wild-type mice in normal control group; B: Wild-type mice in model control group; C: Wild-type mice in mesalazine group; D: Wild-type mice in herbs-partitioned moxibustion group; E: A20IEC-KO mice in normal control group; F: A20IEC-KO mice in model control group; G: A20IEC-KO mice in mesalazine group; H: A20IEC-KO mice in herbs-partitioned moxibustion group. 1: Tissue edema; 2: Hyperemia; 3: Inflammatory cell infiltration; 4: Necrosis; 5: Granulation tissue proliferation; 6: Destruction of glandular structure; 7: Healing ulcer; 8: Ulcer; 9: Proliferation of fibrous tissue.
- Citation: Zhou J, Wu LY, Chen L, Guo YJ, Sun Y, Li T, Zhao JM, Bao CH, Wu HG, Shi Y. Herbs-partitioned moxibustion alleviates aberrant intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis by upregulating A20 expression in a mouse model of Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(17): 2071-2085
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i17/2071.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i17.2071