Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2019; 25(17): 2058-2070
Published online May 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i17.2058
Published online May 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i17.2058
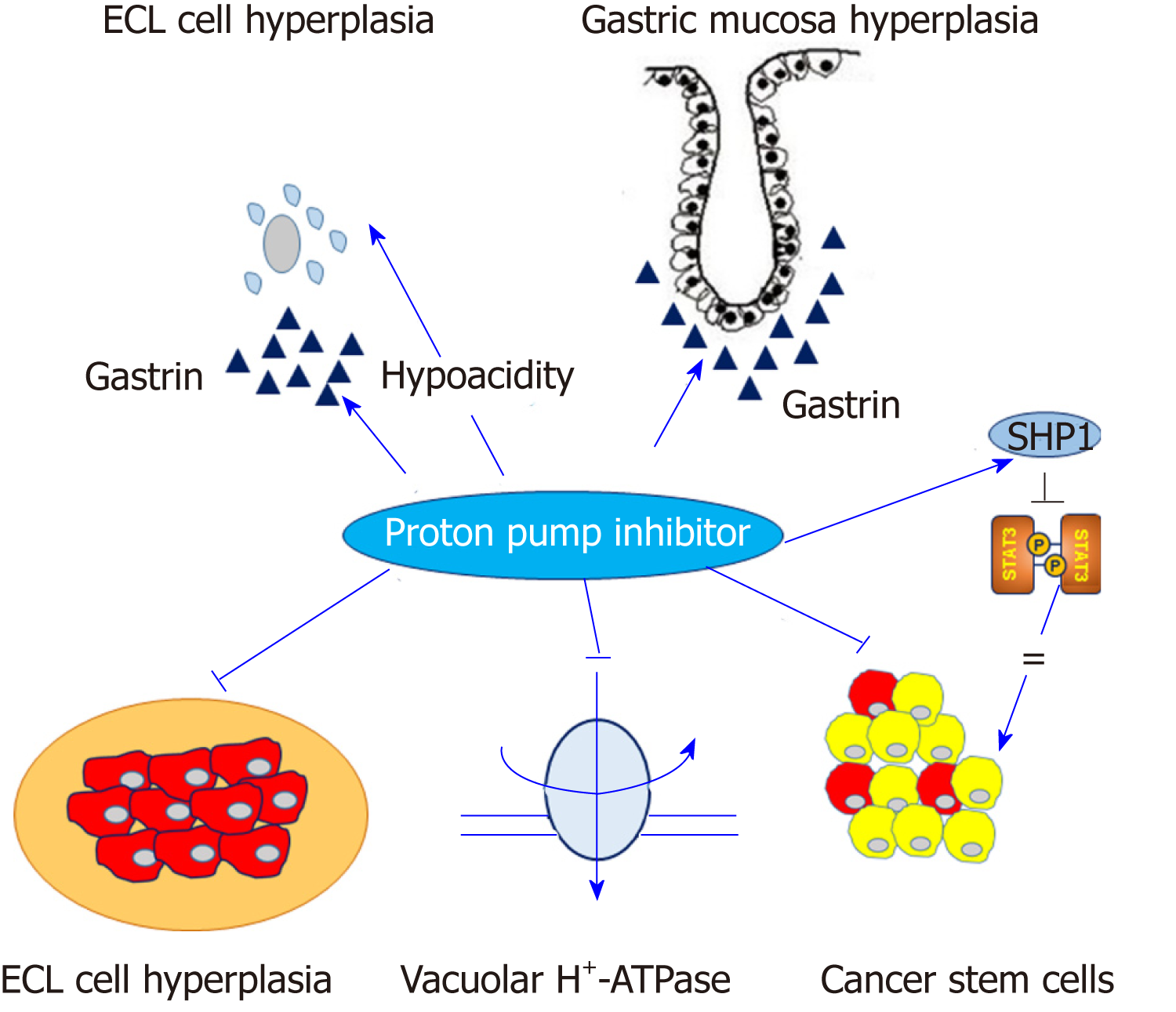
Figure 1 Contrast effects of proton pump inhibitors in normal gastric mucosa and gastric cancer cells.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) induce hypergastrinemia and hypochlorhydria, which may contribute to enterochromaffin-like cell hyperplasia and proliferation of gastric mucosa. Conversely, PPIs may modify the acidic tumor microenvironment and inhibit vacuolar H+-ATPase or signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activity in gastric cancer cells. Arrow indicates the positive effect and straight line indicates the inhibitory effect. ECL: Enterochromaffin-like; SHP1: Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
- Citation: Joo MK, Park JJ, Chun HJ. Proton pump inhibitor: The dual role in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(17): 2058-2070
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i17/2058.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i17.2058