Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2019; 25(16): 1950-1963
Published online Apr 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i16.1950
Published online Apr 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i16.1950
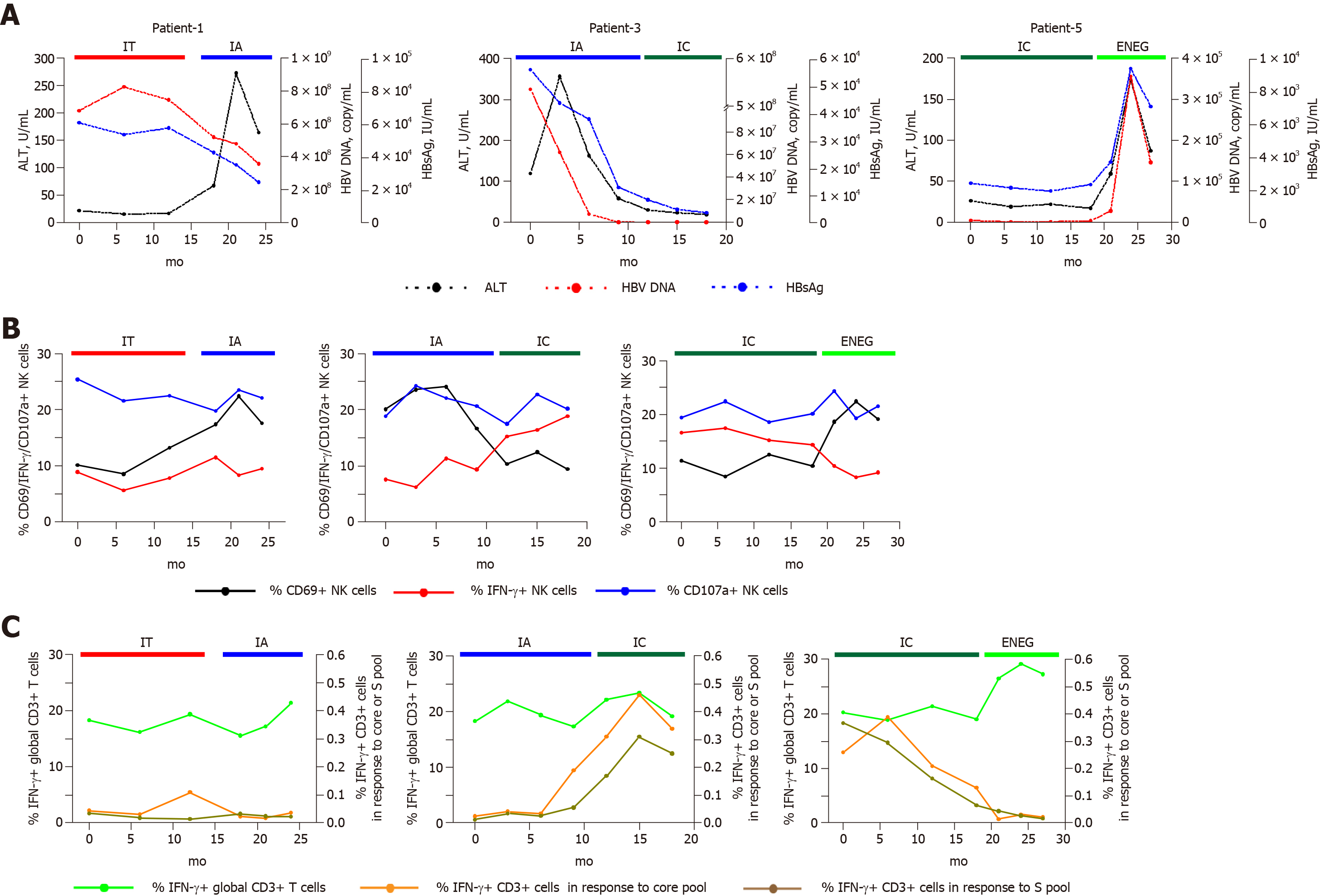
Figure 6 Longitudinal analysis of NK and T cell responses in representative individuals who transitioned from one phase to another.
Patient-1, a patient who transitioned from the immune tolerant to immune active phase. Patient-3, a patient who experienced spontaneous HBeAg clearance. Patient-5, a patient in the clinical phase changed from inactive carrier to HBeAg-negative hepatitis phase. A: Dynamic fluctuations of clinical parameters from one phase to another, including alanine aminotransferase, hepatitis B virus DNA and hepatitis B surface antigen; B: Phenotypic and functional changes of natural killer cells in representative patients who transitioned from one phase to another; C: Changes of interferon-gamma production in global T cells, and core or S peptide pool-stimulated T cells. NK: Natural killer; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; HBeAg: Hepatitis B envelope antigen; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; HD: Healthy honors; IT: Immune tolerant; IA: Immune active; IC: Inactive carrier; ENEG: Hepatitis B envelope antigen-negative hepatitis.
- Citation: Wang WT, Zhao XQ, Li GP, Chen YZ, Wang L, Han MF, Li WN, Chen T, Chen G, Xu D, Ning Q, Zhao XP. Immune response pattern varies with the natural history of chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(16): 1950-1963
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i16/1950.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i16.1950