Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2019; 25(16): 1950-1963
Published online Apr 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i16.1950
Published online Apr 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i16.1950
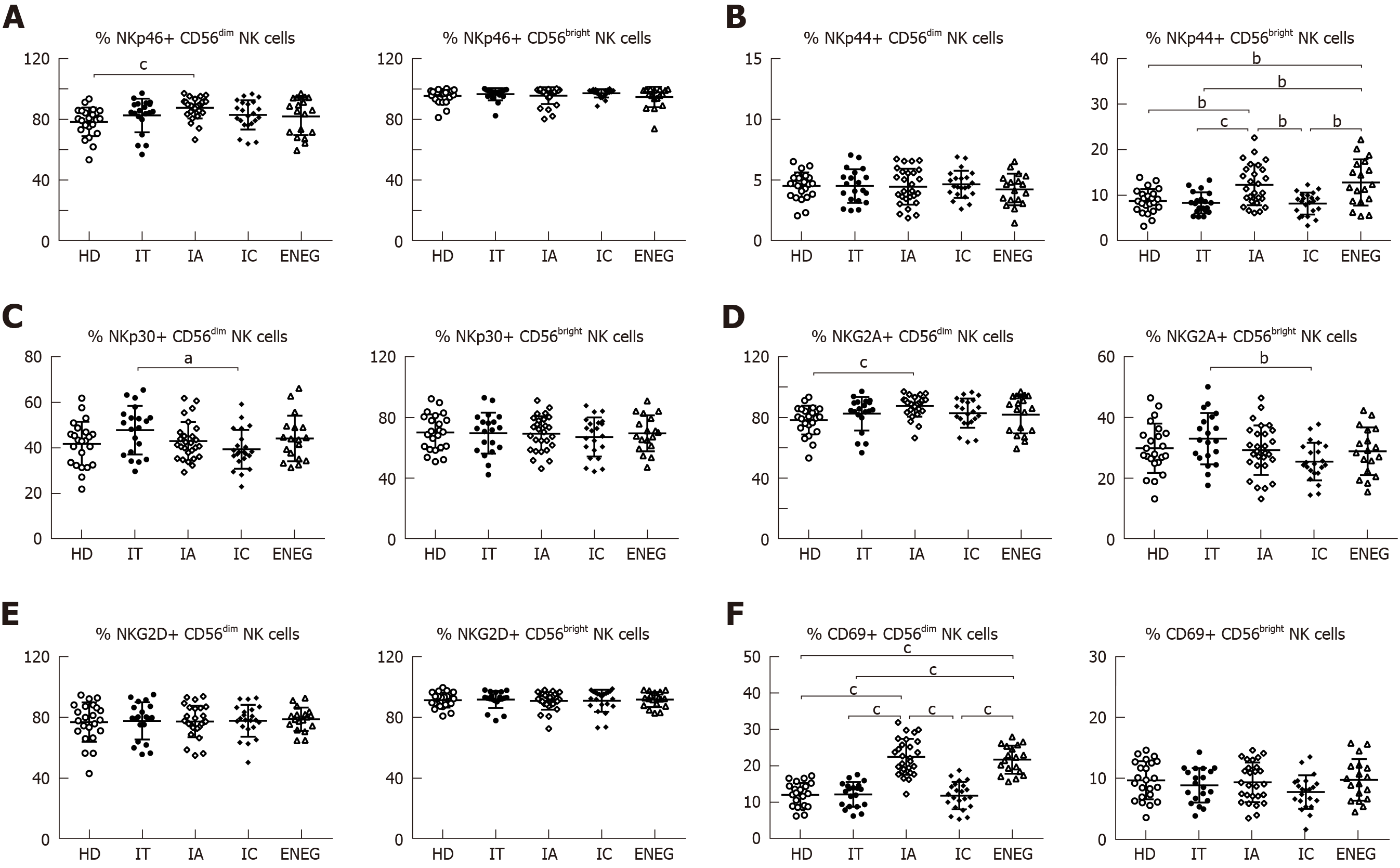
Figure 2 Phenotypes of NK cells in different clinical phases.
A: Frequency of CD56bright and CD56dim NK cells expressing the activating receptor NKp46; B: Frequency of CD56bright and CD56dim NK cells expressing the activating receptor NKp44; C: Frequency of CD56bright and CD56dim NK cells expressing the activating receptor NKp30; D: Frequency of CD56bright and CD56dim NK cells expressing the inhibitory receptor NKG2A; E: Frequency of CD56bright and CD56dim NK cells expressing the activating receptor NKG2D; F: Frequency of CD56bright and CD56dim NK cells expressing the activating marker CD69. NK: Natural killer; HD: Healthy honors; IT: Immune tolerant; IA: Immune active; IC: Inactive carrier; ENEG: Hepatitis B envelope antigen-negative hepatitis. All data are presented as mean ± SD, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
- Citation: Wang WT, Zhao XQ, Li GP, Chen YZ, Wang L, Han MF, Li WN, Chen T, Chen G, Xu D, Ning Q, Zhao XP. Immune response pattern varies with the natural history of chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(16): 1950-1963
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i16/1950.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i16.1950