Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2019; 25(16): 1950-1963
Published online Apr 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i16.1950
Published online Apr 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i16.1950
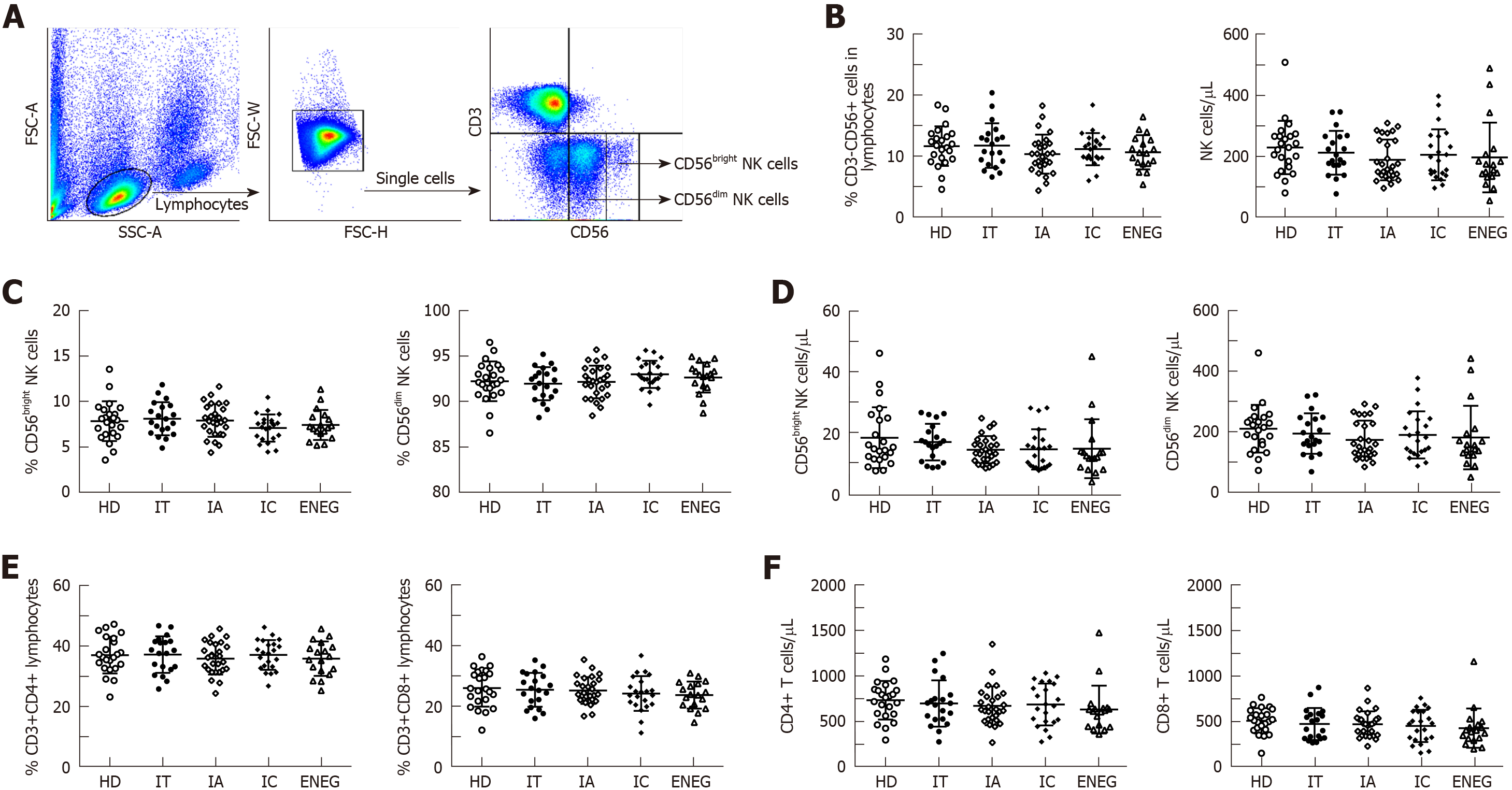
Figure 1 Frequencies and absolute number of NK cells, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in different clinical phases.
A: Representative dot plots depicting the gating strategy for CD3-CD56+ NK cells, CD56bright and CD56dim subsets; B: Frequencies and absolute number of circulating NK cells in different phases; C: Frequencies of CD56bright and CD56dim NK cell subsets in different phases; D: Absolute number of CD56bright and CD56dim NK cell subsets in different phases; E: Frequencies of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in lymphocytes in different phases; F: Absolute number of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in different phases. All data are presented as mean ± SD. NK: Natural killer; HD: Healthy honors; IT: Immune tolerant; IA: Immune active; IC: Inactive carrier; ENEG: Hepatitis B envelope antigen-negative hepatitis.
- Citation: Wang WT, Zhao XQ, Li GP, Chen YZ, Wang L, Han MF, Li WN, Chen T, Chen G, Xu D, Ning Q, Zhao XP. Immune response pattern varies with the natural history of chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(16): 1950-1963
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i16/1950.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i16.1950