Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2019; 25(16): 1913-1927
Published online Apr 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i16.1913
Published online Apr 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i16.1913
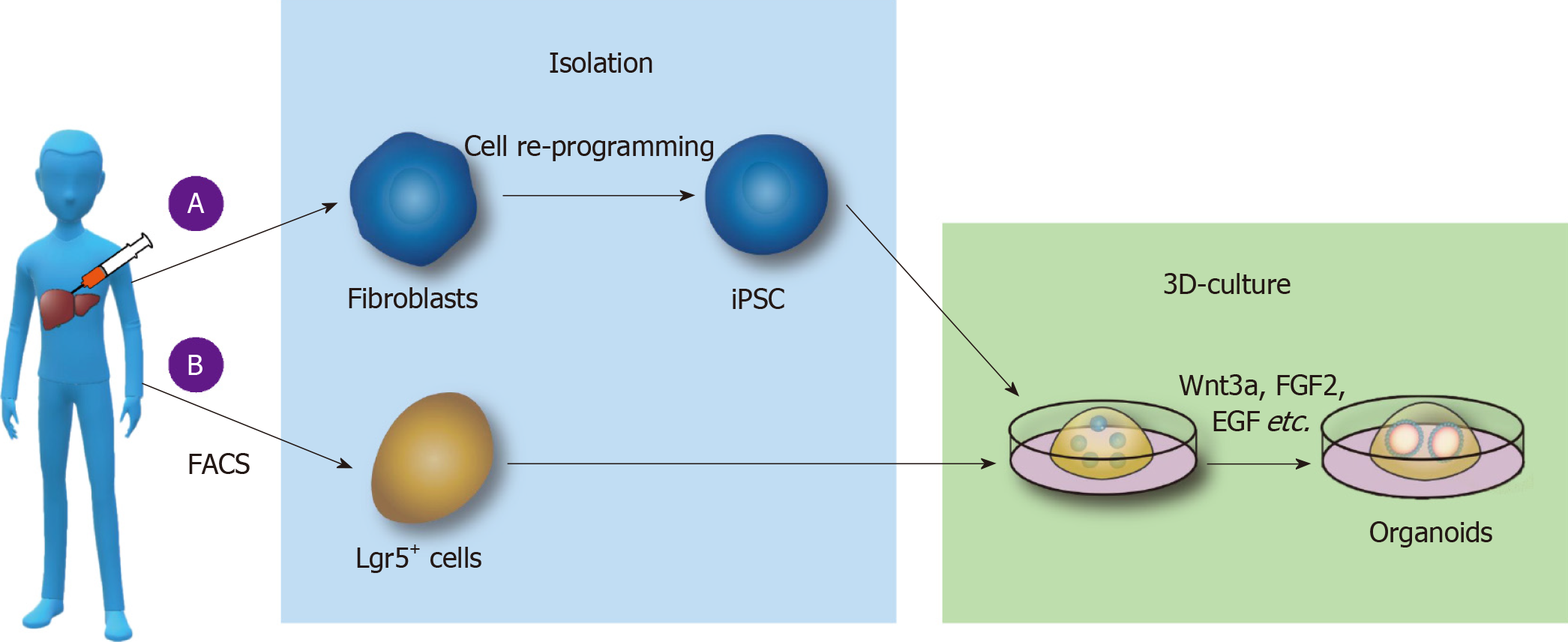
Figure 1 Culture of liver organoids in vitro.
A: Liver organoids cultured from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs). Somatic cells are reprogrammed into induced PSCs; epidermal growth factor (EGF), fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2), and other substances are added to the medium; and the cells are cultured on Matrigel to form liver organoids; B: Liver organoids cultured from adult stem cells. Lgr5+ cells are isolated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting, and Wnt3a, Y27632, EGF, Rspo1, FGF, and other substances are added to form organoids by 3D culture. FACS: Fluorescence-activated cell sorting; iPSCs: Induced pluripotent stem cells; FGF2: Fibroblast growth factor 2; EGF: Epidermal growth factor.
- Citation: Wu LJ, Chen ZY, Wang Y, Zhao JG, Xie XZ, Chen G. Organoids of liver diseases: From bench to bedside. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(16): 1913-1927
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i16/1913.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i16.1913