Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2019; 25(14): 1684-1696
Published online Apr 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i14.1684
Published online Apr 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i14.1684
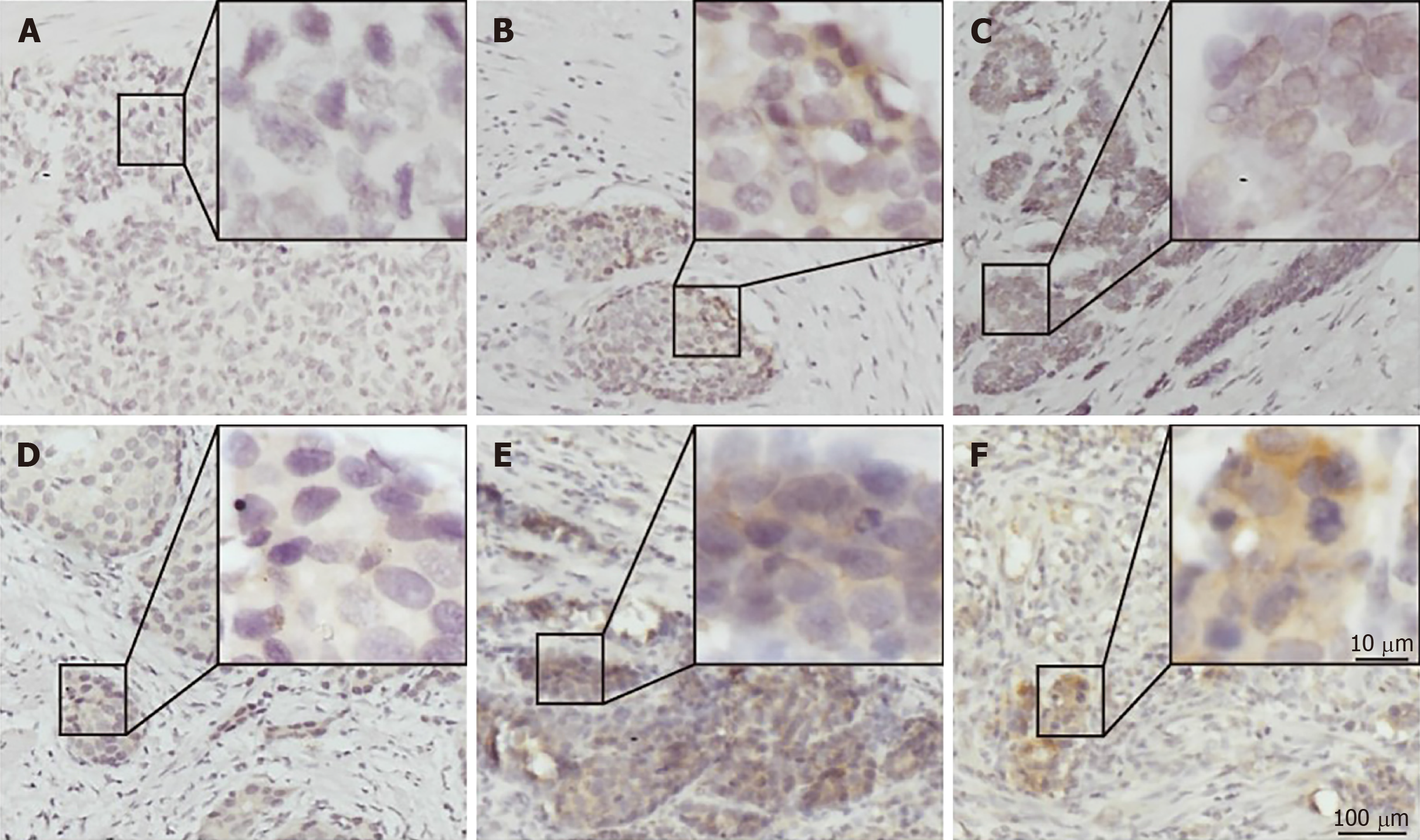
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical staining for programmed death ligand 1 in human gastric neuroendocrine carcinomas.
A: Representative case of negative programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression; B: Tumor-stromal interface enhanced expression of PD-L1; C: Membrane expression of PD-L1; D: Weak staining; E: Moderate staining; F: Strong staining. PD-L1: Programmed death ligand 1.
- Citation: Yang MW, Fu XL, Jiang YS, Chen XJ, Tao LY, Yang JY, Huo YM, Liu W, Zhang JF, Liu PF, Liu Q, Hua R, Zhang ZG, Sun YW, Liu DJ. Clinical significance of programmed death 1/programmed death ligand 1 pathway in gastric neuroendocrine carcinomas. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(14): 1684-1696
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i14/1684.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i14.1684