Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2019; 25(10): 1248-1258
Published online Mar 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i10.1248
Published online Mar 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i10.1248
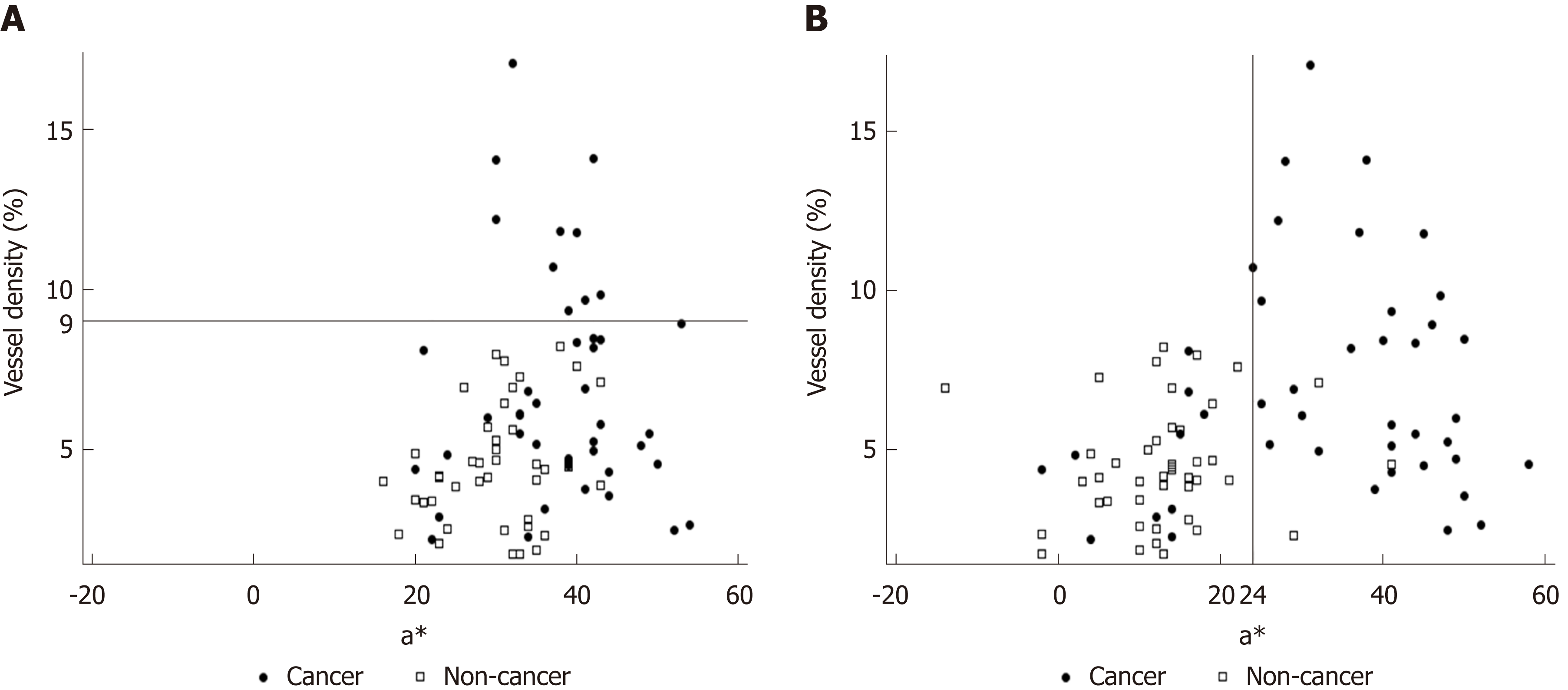
Figure 5 Relationship of a* in Commission Internationale de l'Eclairage 1976 L*a*b* color space (X axis) with blood vessel density from the surface layer to 350 μm (Y axis) using (A) white light imaging (WLI) and (B) linked color imaging (LCI).
Cancer and non-cancer areas were better differentiated with LCI compared to WLI. The blood vessel density was ≥ 9% in all cancer lesions. Using a cut-off value of ≥ 24 for cancer lesions, the diagnostic performance with LCI had sensitivity of 76.7%, specificity of 93.0%, positive predictive value of 91.7%, negative predictive value of 80.0%, and accuracy of 84.9%. WLI: White light imaging; LCI: Linked color imaging.
- Citation: Fujiyoshi T, Miyahara R, Funasaka K, Furukawa K, Sawada T, Maeda K, Yamamura T, Ishikawa T, Ohno E, Nakamura M, Kawashima H, Nakaguro M, Nakatochi M, Hirooka Y. Utility of linked color imaging for endoscopic diagnosis of early gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(10): 1248-1258
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i10/1248.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i10.1248