Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2018; 24(9): 1004-1012
Published online Mar 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i9.1004
Published online Mar 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i9.1004
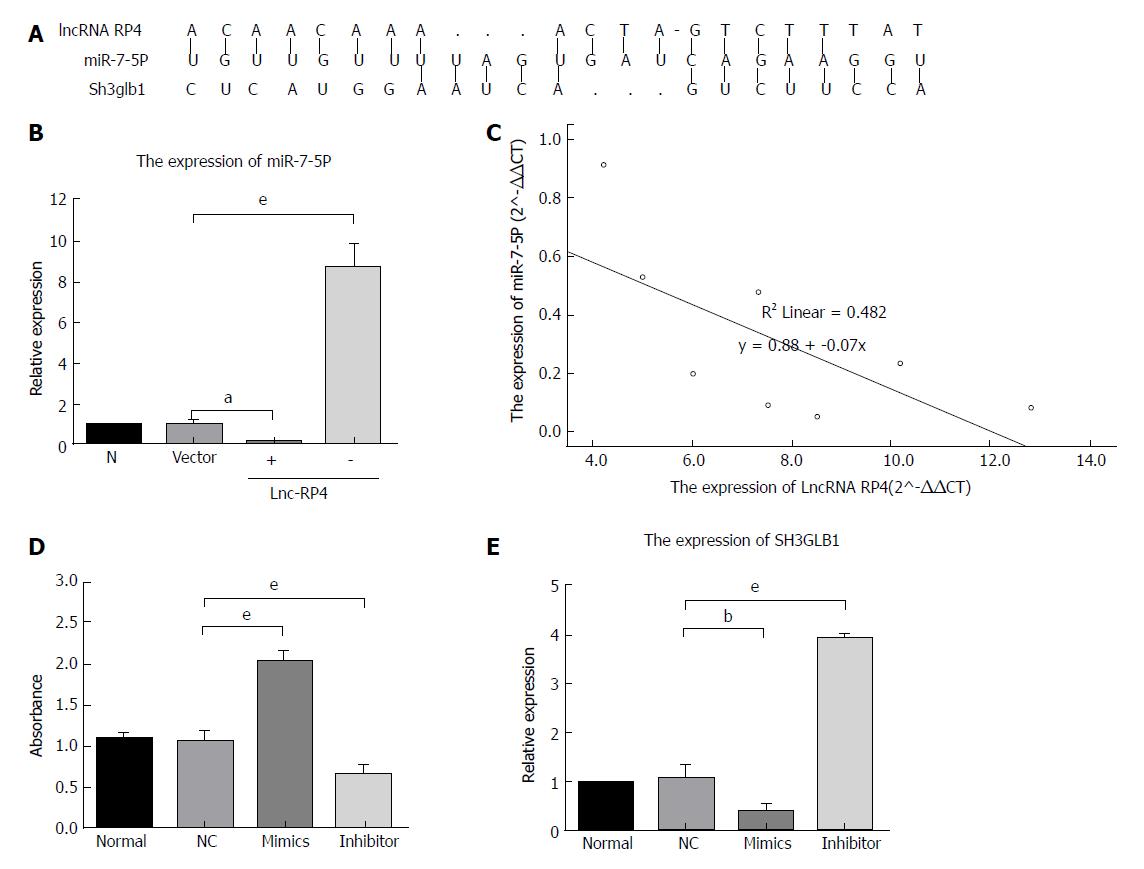
Figure 3 lncRNA RP4 functions as an miR-7-5p decoy in colorectal cancer cells.
A: The predicted miR-7-5p binding sites on the SH3GLB1 and lncRNA RP4 transcript. B: LncRNA RP4 overexpression and knockdown, respectively, decreased and increased the expression of miR-7-5p in SW480 cells. C: Correlation analyses revealed a linear association between the expression of lncRNA RP4 and miR-7-5p, with an r2 value of 0.482. D: SW480 cells were transfected with an miR-7-5p mimic and inhibitor, and cell proliferation was evaluated by the CCK-8 assay. miR-7-5p overexpression and knockdown increased and decreased cell proliferation, respectively. E. Real-time quantitative PCR showed that miR-7-5p overexpression and knockdown, respectively, decreased and increased SH3GLB1 expression level in SW480 colorectal cancer cells. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, and eP < 0.001 for between-group comparisons.
- Citation: Liu ML, Zhang Q, Yuan X, Jin L, Wang LL, Fang TT, Wang WB. Long noncoding RNA RP4 functions as a competing endogenous RNA through miR-7-5p sponge activity in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(9): 1004-1012
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i9/1004.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i9.1004