Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2018; 24(7): 819-832
Published online Feb 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i7.819
Published online Feb 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i7.819
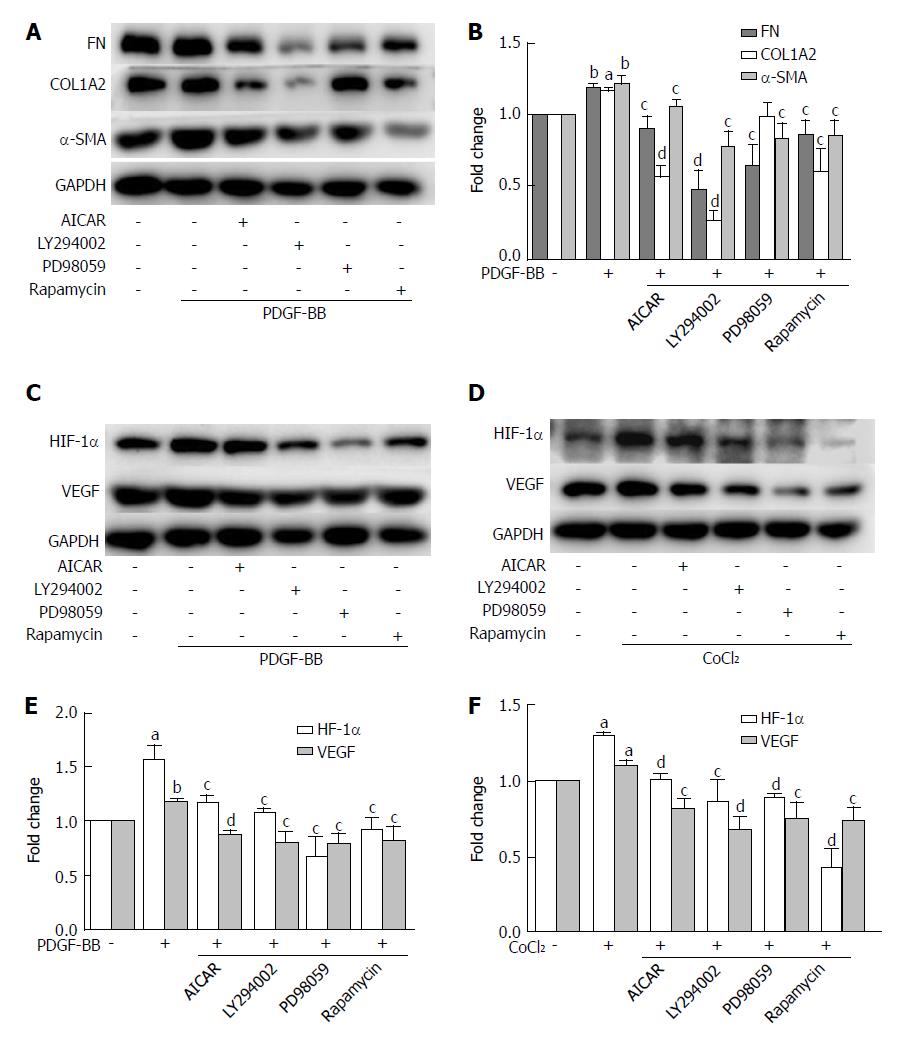
Figure 7 The inhibitory effects of metformin on activated hepatic stellate cells were associated with activation of AMPK and subsequent down-regulation of the Akt/mTOR and ERK signaling pathways.
A and B: HSCs were pretreated with AICAR (500 μmol/L), LY294002 (20 μmol/L), PD98059 (10 μmol/L), or rapamycin (100 nmol/L) for 2 h and then incubated with PDGF-BB (10 ng/mL) for 24 h. Expression levels of fibronectin (FN), collagen type I (COL1A2), and α-SMA were measured by Western blot analysis and the results were quantified; C and D: HSCs were pretreated with AICAR (500 μmol/L), LY294002 (20 μmol/L), PD98059 (10 μmol/L), or rapamycin (100 nmol/L) for 2 h and then incubated with or without CoCl2 (150 μmol/L) for 12 h. Expression levels of HIF-1α and VEGF were measured by Western blot analysis; E and F: The results were quantified. (aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs the control group, cP < 0.05 and dP < 0.01 vs the PDGF-BB or CoCl2 only groups). HSCs: Hepatic stellate cells.
- Citation: Li Z, Ding Q, Ling LP, Wu Y, Meng DX, Li X, Zhang CQ. Metformin attenuates motility, contraction, and fibrogenic response of hepatic stellate cells in vivo and in vitro by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(7): 819-832
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i7/819.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i7.819