Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2018; 24(7): 819-832
Published online Feb 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i7.819
Published online Feb 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i7.819
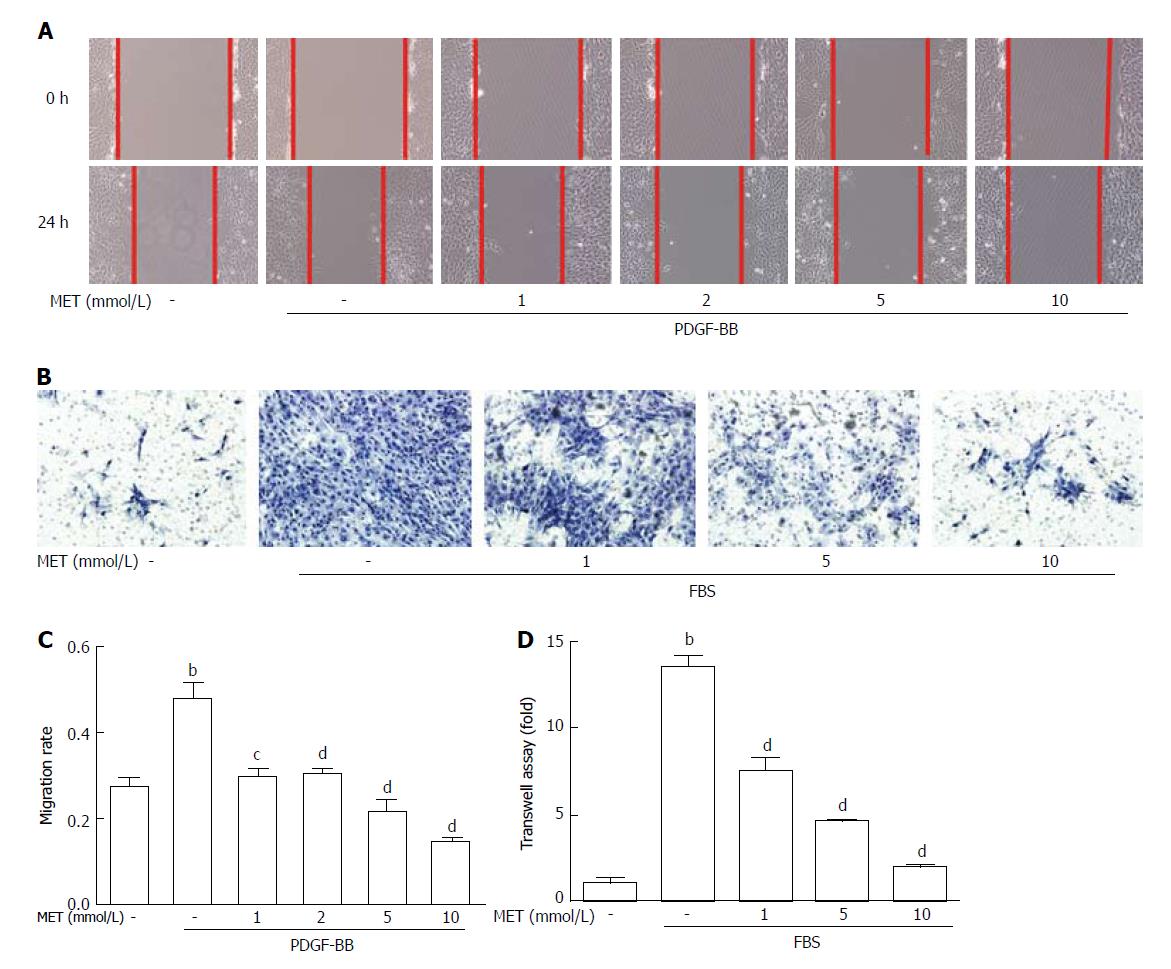
Figure 3 Effect of metformin on hepatic stellate cell migration and invasion.
Scratch tests were used to determine cell migration, and Transwell assays were used to evaluate cell invasion. A: HSCs were scraped and then incubated with or without PDGF-BB (10 ng/mL) and metformin (1, 2, 5, and 10 mmol/L). Images were acquired at 0 and 24 h (100 × magnification); B: HSCs were seeded in the upper chamber with a Matrigel membrane, and various concentrations of metformin (0, 1, 5, and 10 mmol/L) were added to the medium. The lower chambers were loaded with DMEM with or without 10% FBS. Cells that migrated through the membrane were fixed and stained with hematoxylin at 24 h; C: The migration ability was quantified by measuring the distance of the scratch edge; D: Cells that migrated through the membrane were counted and quantified. (bP < 0.01 vs the control group, cP < 0.05 and dP < 0.01 vs the PDGF-BB or FBS only groups). HSCs: Hepatic stellate cells.
- Citation: Li Z, Ding Q, Ling LP, Wu Y, Meng DX, Li X, Zhang CQ. Metformin attenuates motility, contraction, and fibrogenic response of hepatic stellate cells in vivo and in vitro by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(7): 819-832
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i7/819.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i7.819