Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2018; 24(7): 819-832
Published online Feb 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i7.819
Published online Feb 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i7.819
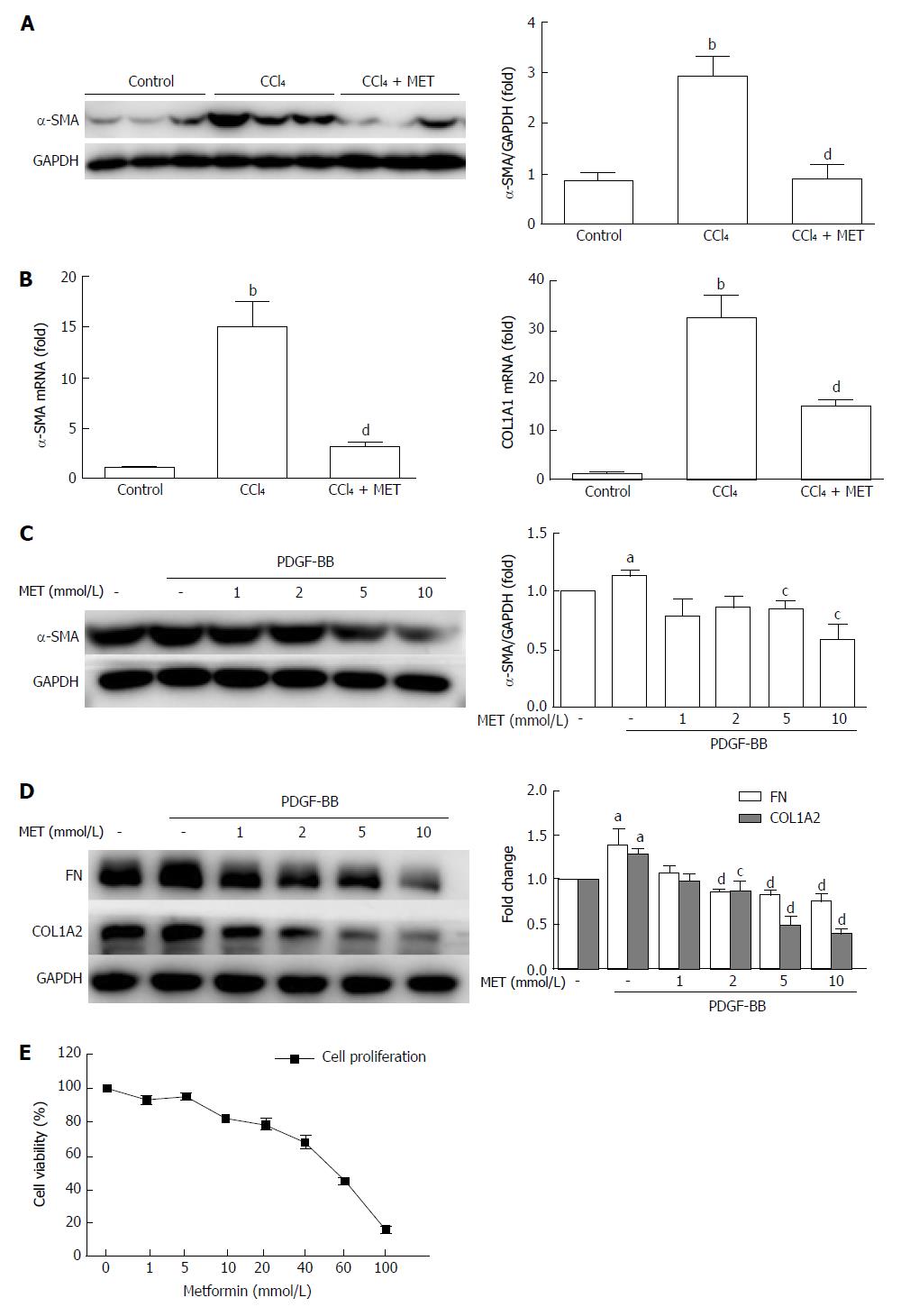
Figure 2 Effect of metformin on the activation, proliferation, and extracellular matrix secretion of hepatic stellate cells.
A: Measurement of α-SMA levels in murine liver tissues by Western blot; B: Measurement of hepatic α-SMA and collagen type I mRNA expression levels by quantitative real-time PCR (n = 5, bP < 0.01 vs the control group, dP < 0.01 vs the CCl4 group); C and D: HSCs were treated with or without 10 ng/mL PDGF-BB for 24 h, and the effect of metformin (1, 2, 5, and 10 mmol/L) on the expression levels of α-SMA, collagen type I, and fibronectin (FN) were measured by Western blot (aP < 0.05 vs the control group, cP < 0.05 and dP < 0.01 vs the PDGF-BB only group); E: HSCs were treated with a series of concentrations ranging from 1 mmol/L to 100 mmol/L of metformin for 24 h, and the proliferation was measured by CCK-8 assays. HSCs: Hepatic stellate cells.
- Citation: Li Z, Ding Q, Ling LP, Wu Y, Meng DX, Li X, Zhang CQ. Metformin attenuates motility, contraction, and fibrogenic response of hepatic stellate cells in vivo and in vitro by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(7): 819-832
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i7/819.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i7.819