Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2018; 24(6): 693-705
Published online Feb 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i6.693
Published online Feb 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i6.693
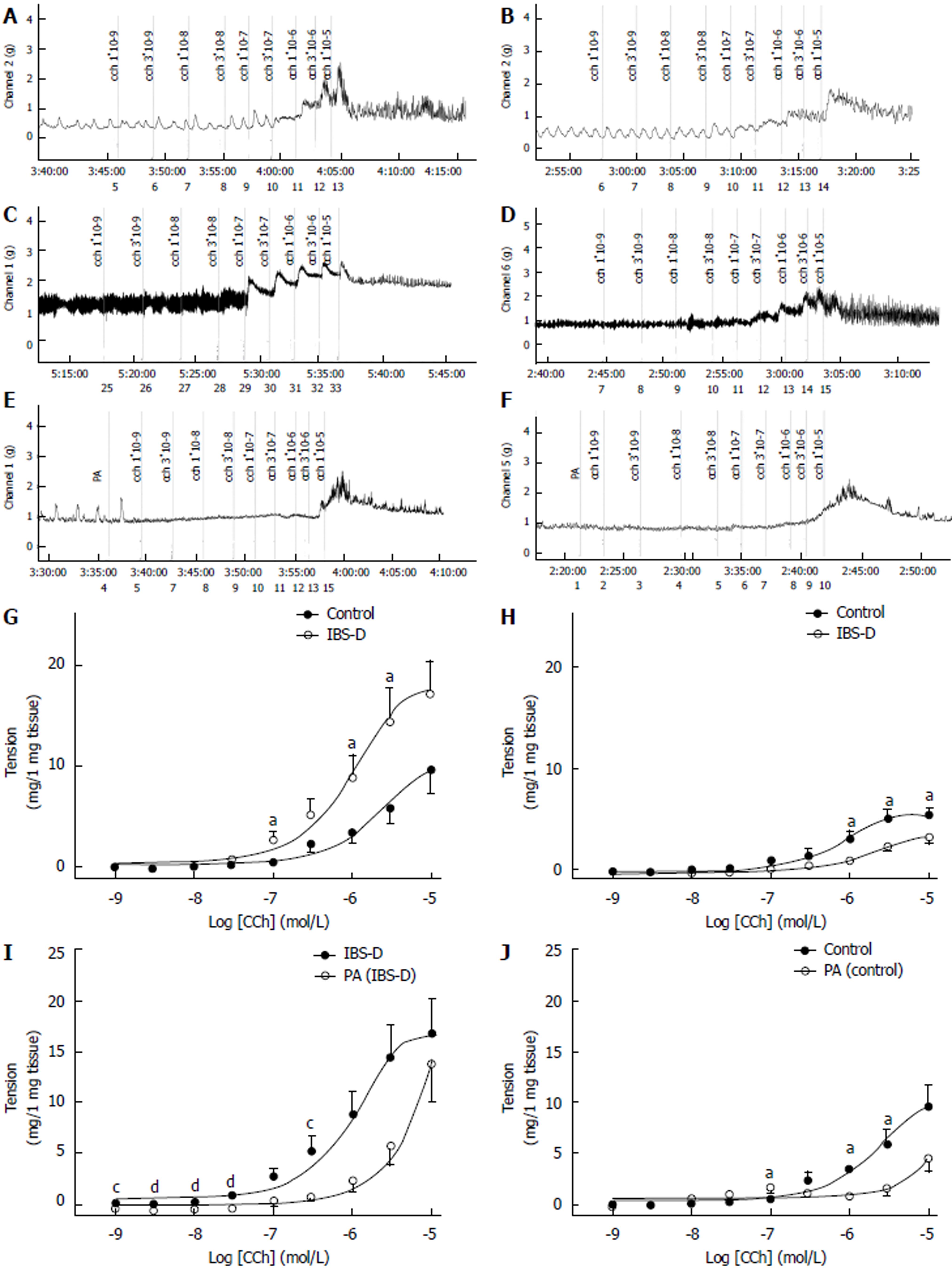
Figure 4 Inhibitory effects of PA on CCh-induced contraction in the isolated colonic longitudinal smooth muscle.
Mechanical recording (A to F) and cumulative log concentration-response curve (G) of CCh-induced contraction of the smooth muscle in IBS-D rats. Colonic tissues (control group [A]: n = 14, IBS-D group [B]: n = 16; aP < 0.05 vs control group, unpaired t test). Jejunal tissues (H) (control group [C]: n = 14, IBS-D group [D]: n = 11; aP < 0.05 vs control group, unpaired t test). Cumulative log concentration-response curve (I) of the effect of PA (100 µmol/L) on CCh-induced contraction of smooth muscle in IBS-D rats. Colonic tissues (IBS-D group: n = 16, PA-treated IBS-D group [F]: n = 8; cP < 0.05 vs group IBS-D, dP < 0.01 vs group IBS-D, unpaired t test). Cumulative log concentration-response curve (J) of the effect of PA (100 µmol/L) on CCh-induced contraction of the smooth muscle in control rats. Colonic tissues (control group: n = 14, PA-treated control group [E]: n = 8. aP < 0.05 vs control group, bP < 0.01 vs control group, unpaired t test). Data are expressed as mean ± SE. CCh: Carbachol, IBS-D: Irritable bowel syndrome; PA: Patchouli alcohol.
- Citation: Zhou TR, Huang JJ, Huang ZT, Cao HY, Tan B. Inhibitory effects of patchouli alcohol on stress-induced diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(6): 693-705
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i6/693.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i6.693