Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2018; 24(6): 680-692
Published online Feb 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i6.680
Published online Feb 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i6.680
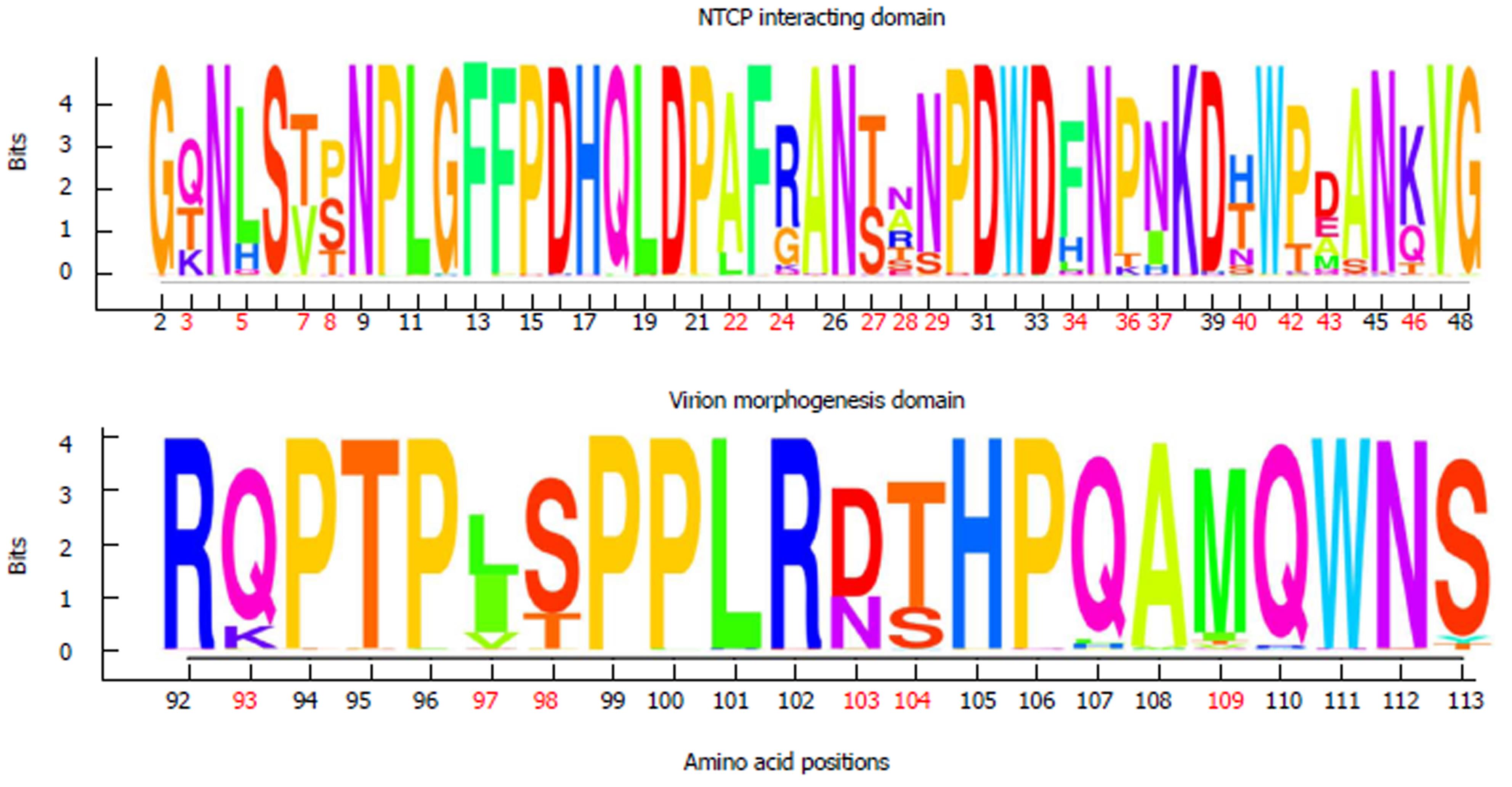
Figure 3 Sequence logos showing the information content of amino acid positions from the sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide-interacting domain and the virion morphogenesis domain, in all the haplotypes obtained by next-generation sequencing.
In order to simplify variations due to HBV genotype, the numeration of aa positions from both domains is presented according to genotype D: NTCP-interacting domain from residues 2 to 48 of the N-terminal end of preS1, and the virion morphogenesis domain from residues 92 to 108 of the C-terminal end of preS1 and first 5 residues from the N-terminal end of preS2. Positions where the wild-type aa varies according to HBV genotype have been highlighted in bold and red. aa: Amino acid; NTCP: Sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide.
- Citation: Casillas R, Tabernero D, Gregori J, Belmonte I, Cortese MF, González C, Riveiro-Barciela M, López RM, Quer J, Esteban R, Buti M, Rodríguez-Frías F. Analysis of hepatitis B virus preS1 variability and prevalence of the rs2296651 polymorphism in a Spanish population. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(6): 680-692
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i6/680.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i6.680