Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2018; 24(6): 657-670
Published online Feb 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i6.657
Published online Feb 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i6.657
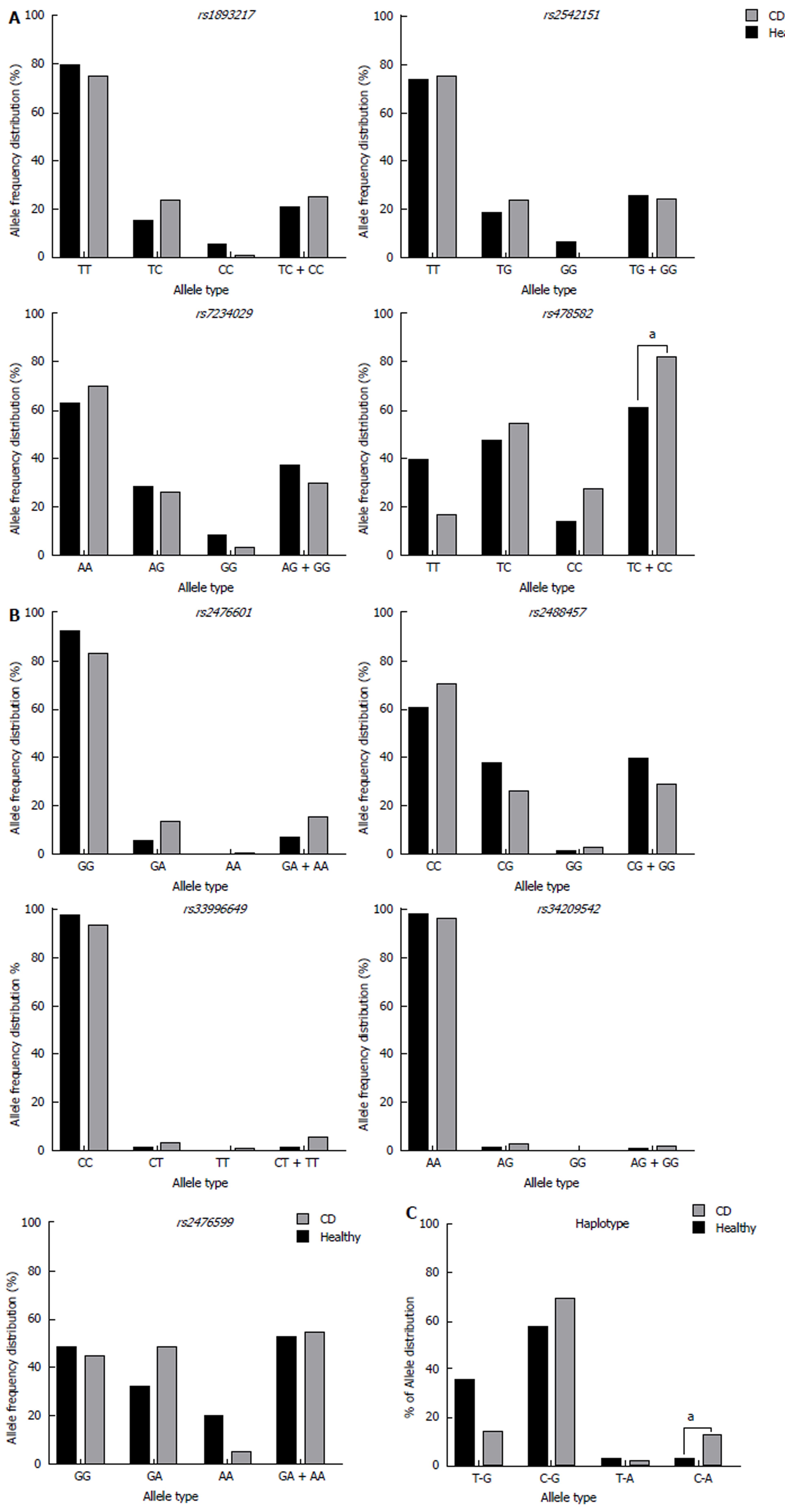
Figure 2 Allele frequency in nine single nucleotide polymorphisms in crohn’s disease and healthy control subjects.
A: Represents allele frequency of PTPN2 SNPs: rs1893217, rs2542151, rs7234029, rs478582; B: Represents allele frequency of PTPN22 SNPs: rs2476601, rs2488457, rs33996649, rs34209542, rs2476599; C: Represents haplotype combinations PTPN2:rs478582 and PTPN22:rs2476601. aP < 0.05, healthy vs CD. T-G: Major/major; C-G: SNP/major; T-A: Major/SNP; C-A: SNP/SNP; SNPs: Single nucleotide polymorphisms; CD: Crohn’s disease; PTPN2: Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2; PTPN22: Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 22.
- Citation: Sharp RC, Beg SA, Naser SA. Role of PTPN2/22 polymorphisms in pathophysiology of Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(6): 657-670
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i6/657.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i6.657