Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2018; 24(48): 5491-5504
Published online Dec 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5491
Published online Dec 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5491
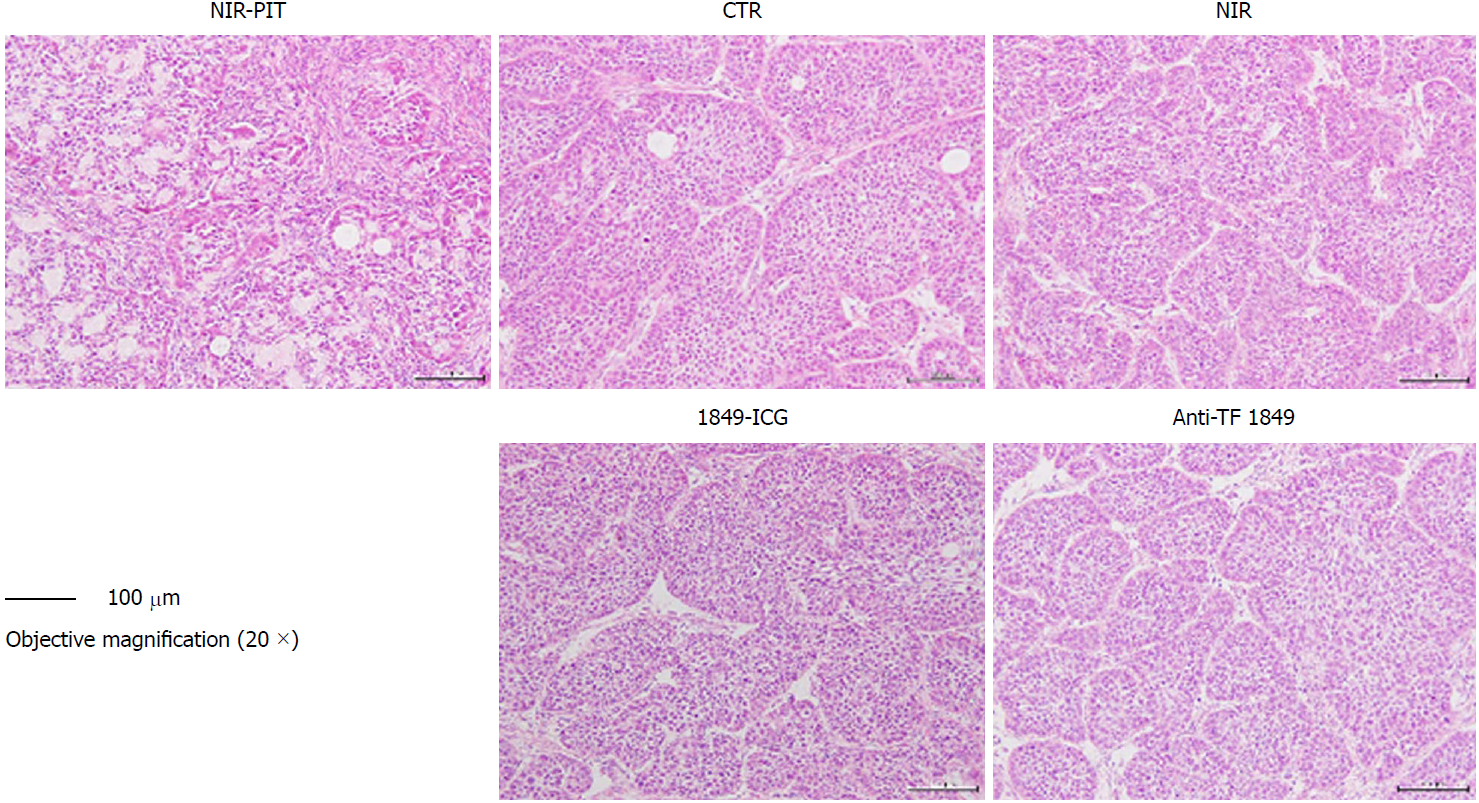
Figure 6 Histological examination of effects of near-infrared photoimmunotherapy 72 h after 2nd exposure to near-infrared light.
Tumors were resected and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. After near-infrared photoimmunotherapy (NIR-PIT), tumors showed necrotic death-associated features including loss of tumor cells and cells nest pattern, scattering of damaged and hypertrophic tumor cells, and abundant fibrosis. No obvious damage was detected in the tumors of other control groups; receiving no treatment, NIR light alone, indocyanine green-labeled anti-tissue factor (TF) antibody 1849 (1849-ICG) alone and anti-TF antibody 1849 (anti-TF 1849) alone. Photos of tumor section were taken under 20 × objective magnification (scale bar = 100 μm). Anti-TF 1849: Anti-tissue factor antibody 1849; CTR: Control; 1849-ICG: Indocyanine green-labeled anti-tissue factor antibody 1849; NIR: Near-infrared; PIT: Photoimmunotherapy.
- Citation: Aung W, Tsuji AB, Sugyo A, Takashima H, Yasunaga M, Matsumura Y, Higashi T. Near-infrared photoimmunotherapy of pancreatic cancer using an indocyanine green-labeled anti-tissue factor antibody. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(48): 5491-5504
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i48/5491.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5491