Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2018; 24(48): 5477-5490
Published online Dec 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5477
Published online Dec 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5477
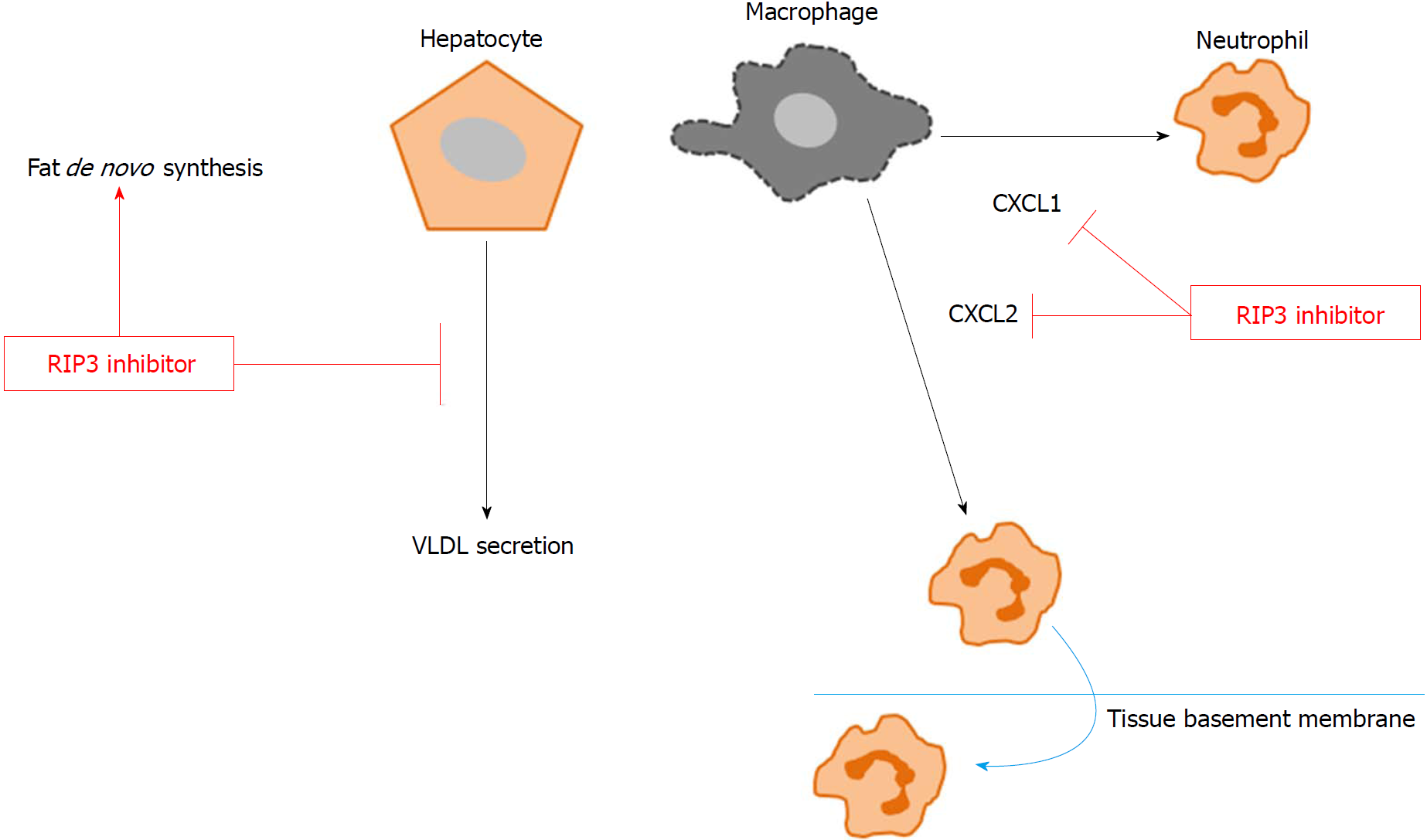
Figure 6 Conceptual diagram.
GSK'843 treatment decreases neutrophil recruitment markers, including CXCL1 and CXCL2, thereby reducing neutrophil recruitment to the tissue. However, RIP3 inhibition increases de novo fat synthesis while decreasing VLDL secretion. RIP3: Receptor interacting protein kinase-3; CXCL1: Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand-1; CXCL2: Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand-2; VLDL: Very-low-density lipoproteins.
- Citation: Saeed WK, Jun DW, Jang K, Ahn SB, Oh JH, Chae YJ, Lee JS, Kang HT. Mismatched effects of receptor interacting protein kinase-3 on hepatic steatosis and inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(48): 5477-5490
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i48/5477.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5477