Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2018; 24(48): 5477-5490
Published online Dec 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5477
Published online Dec 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5477
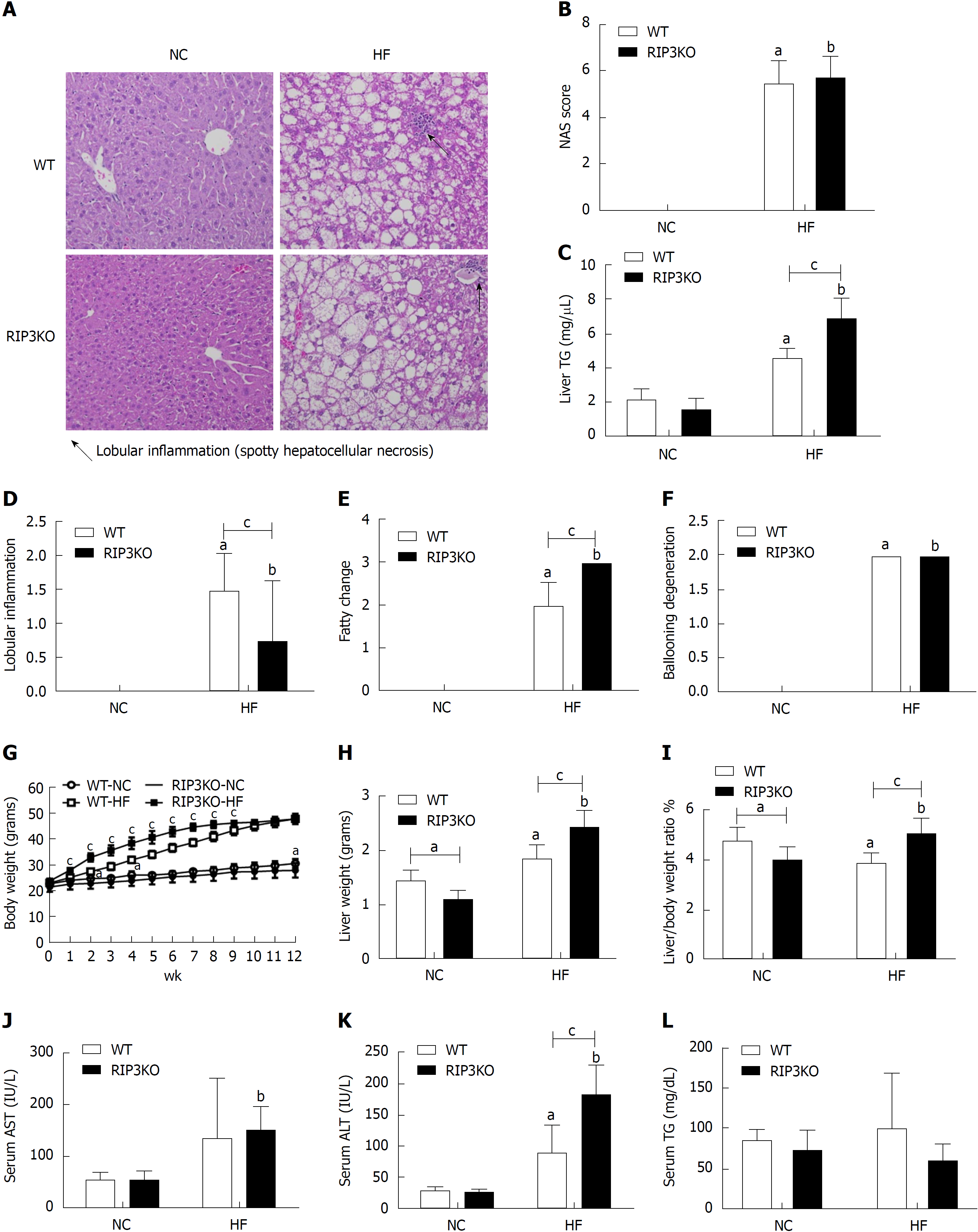
Figure 1 Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 deletion exacerbates HF diet induced steatosis.
A: Following 12-wk HF diet, the liver tissue hematoxylin & eosin staining showed increased steatosis in RIP3KO-HF group compared to WT-HF group. B-F: Liver TG contents were significantly increased in the RIP3KO-HF group compared to the WT-HF group. RIP3KO-HF group had increased steatosis and decreased lobular inflammation. G-L: HF diet fed RIP3KO mice had increased liver weight and liver/body weight ratio compared to HF diet fed WT mice. The RIP3KO-HF group had increased serum AST and ALT but decreased serum TG compared to the WT-HF group. aP < 0.05 by Mann-Whitney U test, compared to NC diet fed WT group; bP < 0.05 by Mann-Whitney U test, compared to NC diet fed RIP3-KO group; cP < 0.05 by Mann-Whitney U test, compared to HF diet fed WT group. HF: High fat; NC: Normal chow; WT: Wild-type; KO: Knockout; RIP3: Receptor interacting protein kinase-3; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; TG: Triglycerides.
- Citation: Saeed WK, Jun DW, Jang K, Ahn SB, Oh JH, Chae YJ, Lee JS, Kang HT. Mismatched effects of receptor interacting protein kinase-3 on hepatic steatosis and inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(48): 5477-5490
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i48/5477.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5477