Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2018; 24(48): 5462-5476
Published online Dec 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5462
Published online Dec 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5462
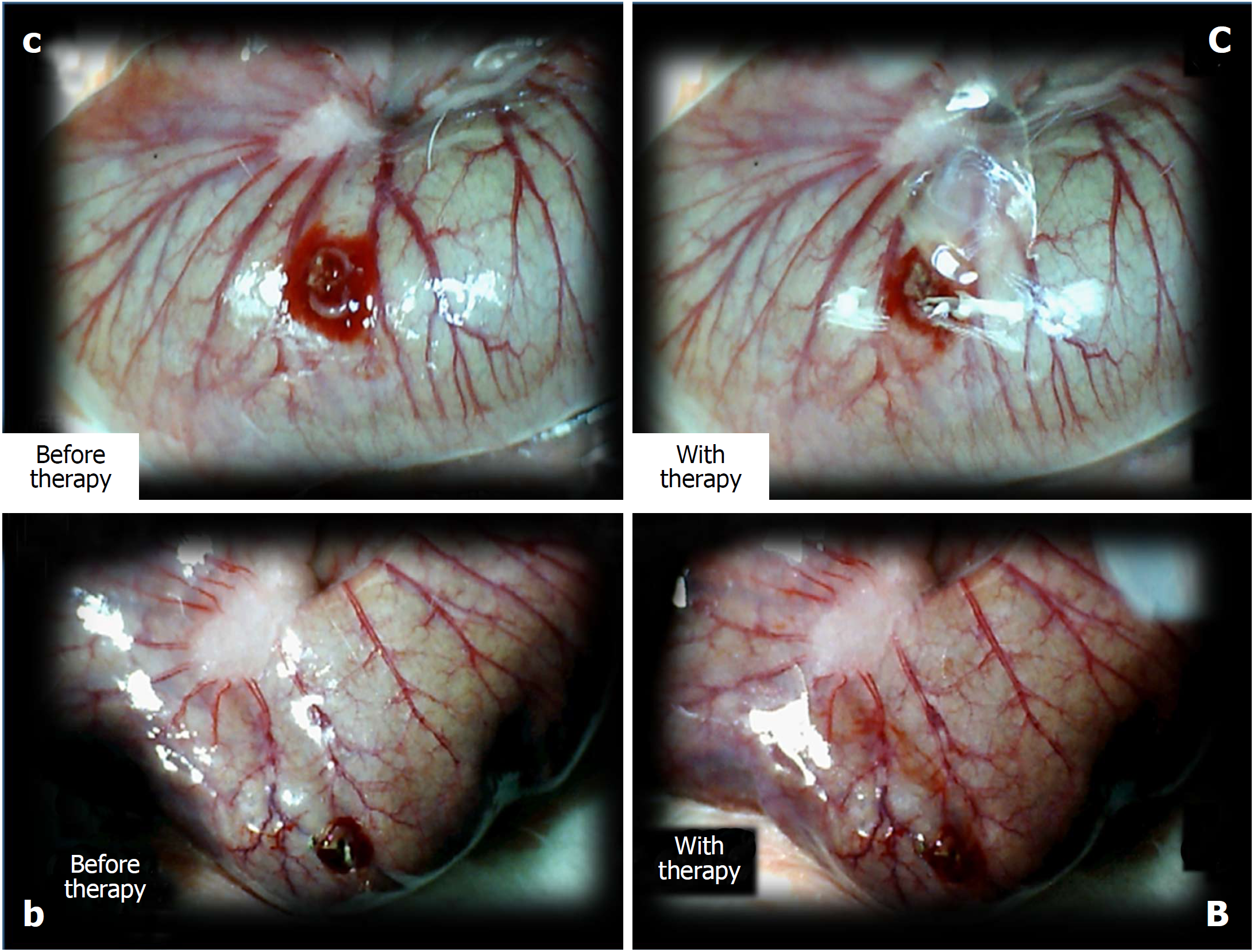
Figure 6 The perforated cecum.
Perforate lesions, before therapy (c, b) (left). Perforate lesions with therapy [control, saline (C), BPC 157 (B)] (right). Illustrative distinctive effect of medication administration (saline bath (right, upper, control (C) vs BPC 157 bath [right, low, BPC 157 (B)]. Regular failing effect of saline bath application on vessels presentation [right, upper, control (C)] vs the immediate recruitment effect of BPC 157 bath administration on the blood vessels presentation toward the perforated injury [right, low, BPC 157 (B)]. Note the initial recovery of blood vessels that appear alongside with the BPC 157 bath, a network raising toward the perforated defect.
- Citation: Drmic D, Samara M, Vidovic T, Malekinusic D, Antunovic M, Vrdoljak B, Ruzman J, Milkovic Perisa M, Horvat Pavlov K, Jeyakumar J, Seiwerth S, Sikiric P. Counteraction of perforated cecum lesions in rats: Effects of pentadecapeptide BPC 157, L-NAME and L-arginine. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(48): 5462-5476
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i48/5462.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5462