Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2018; 24(48): 5462-5476
Published online Dec 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5462
Published online Dec 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5462
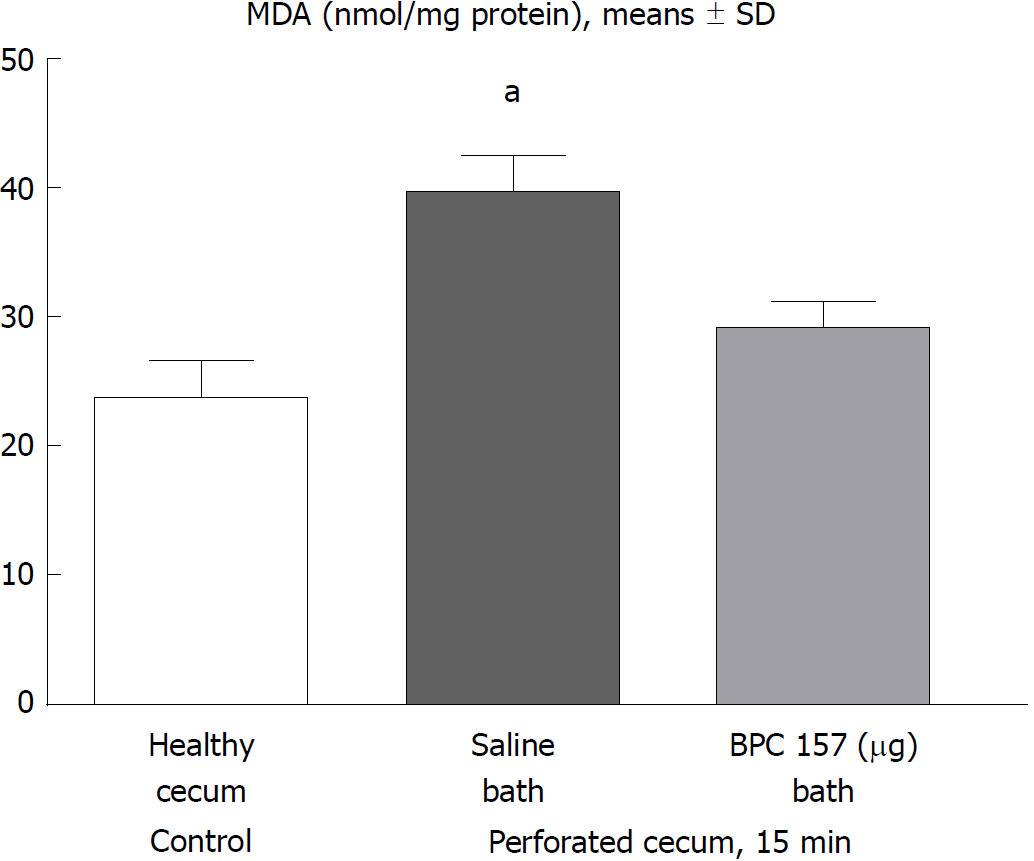
Figure 5 At 15 min post-injury, oxidative stress in tissue samples was assessed by quantifying thiobarbituric acid reactivity as malondialdehyde equivalents.
Administration of medication (/kg, 10 mL/2 min bath/rat) at the perforated (5 mm diameter) cecum lesion and cecum was BPC 157 (10 μg) or a saline bath of equal volume (controls). Minimum aP < 0.05 vs control. MDA: Malondialdehyde equivalents.
- Citation: Drmic D, Samara M, Vidovic T, Malekinusic D, Antunovic M, Vrdoljak B, Ruzman J, Milkovic Perisa M, Horvat Pavlov K, Jeyakumar J, Seiwerth S, Sikiric P. Counteraction of perforated cecum lesions in rats: Effects of pentadecapeptide BPC 157, L-NAME and L-arginine. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(48): 5462-5476
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i48/5462.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5462