Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2018; 24(48): 5462-5476
Published online Dec 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5462
Published online Dec 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5462
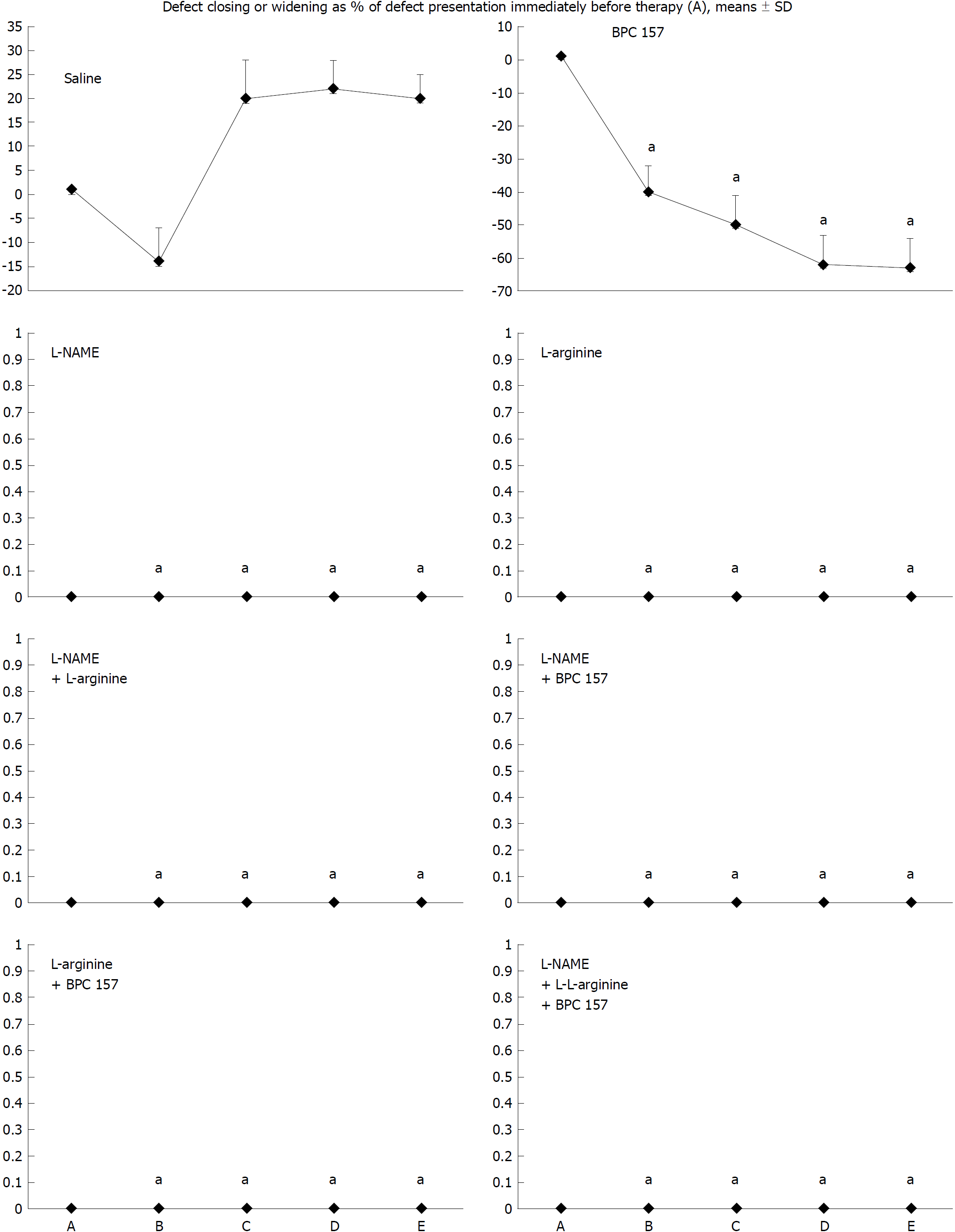
Figure 2 Defect closing or widening [both as % of presentation immediately before therapy (A)]; bleeding time (s); A: after perforation (1 min); B: during application (2 min); C: the period after application (2 min); D: the subsequent 5-min period; E: the period until the end of the observation (15 min).
At 1 min post-injury, administration of medication (/kg, 10 mL/2 min bath/rat) at the perforated (5 mm diameter) cecum lesion and cecum (M-mucosa; S-serosa), including BPC 157 (10 μg), NOS blocker L-NAME (5 mg), NOS substrate L-arginine (100 mg) alone or combined, and a saline bath equal volume (controls). Rats were then left after abdominal closure undisturbed until sacrifice, at day 1 or day 7. aP < 0.05 at least vs control.
- Citation: Drmic D, Samara M, Vidovic T, Malekinusic D, Antunovic M, Vrdoljak B, Ruzman J, Milkovic Perisa M, Horvat Pavlov K, Jeyakumar J, Seiwerth S, Sikiric P. Counteraction of perforated cecum lesions in rats: Effects of pentadecapeptide BPC 157, L-NAME and L-arginine. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(48): 5462-5476
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i48/5462.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5462