Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2018; 24(48): 5462-5476
Published online Dec 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5462
Published online Dec 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5462
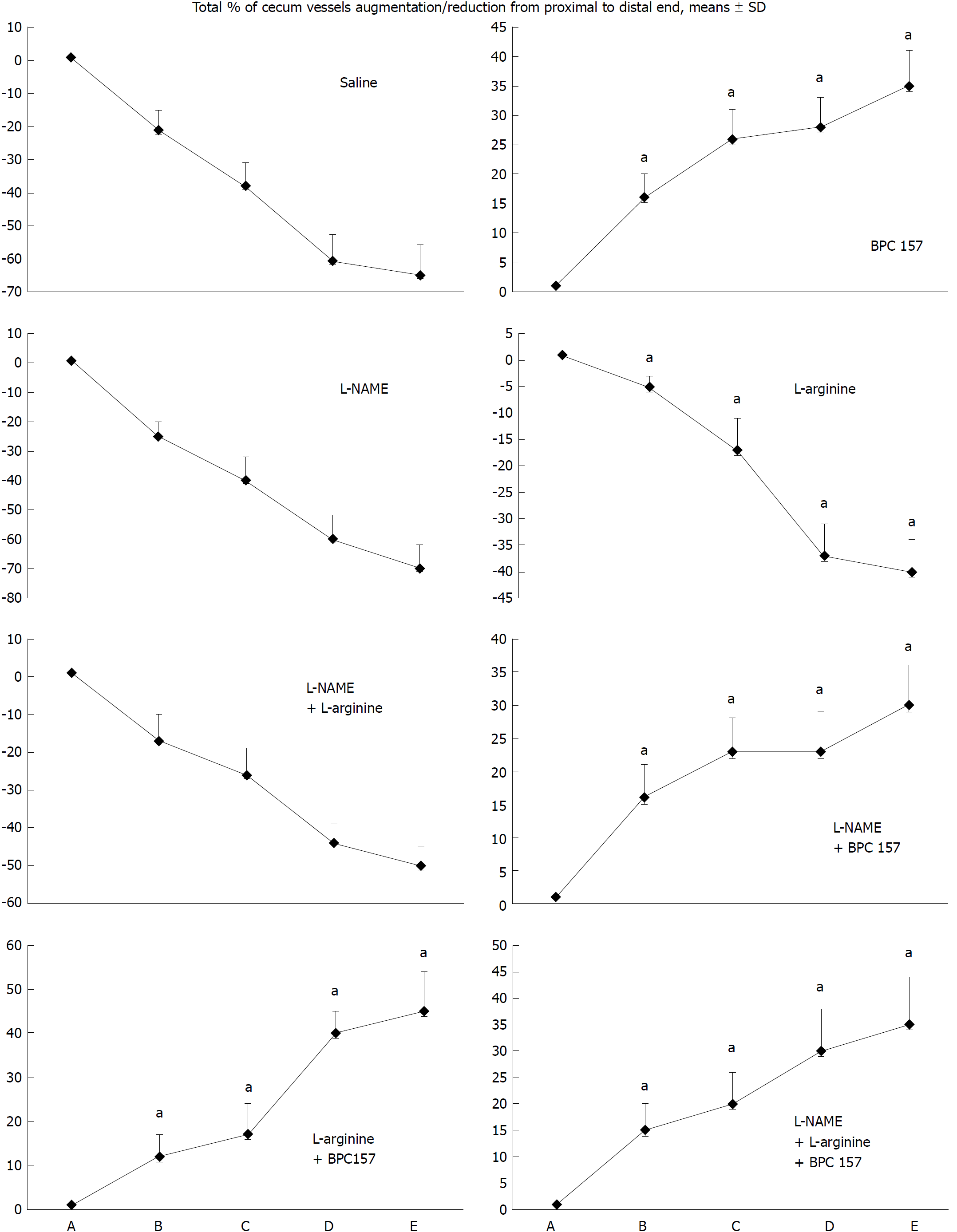
Figure 1 Blood vessels, filled/appearance or cleared out/disappearance (assessed with a USB microscope camera, Veho discovery VMS-004D-400x USB microscope), as [total % of cecum vessels augmentation/reduction from proximal to distal end = [number of blood vessels (10 vessels assessed) /100] x % of augmentation/reducing of each vasa recta (0 as point immediately before therapy) (A)].
A: after perforation (1 min); B: during application (2 min); C: the period after application (2 min); D: the subsequent 5-min period; E: the period until the end of the observation (15 min). At 1 min post-injury, medication (/kg, 10 mL/2 min bath/rat) administered at the perforated (5 mm diameter) cecum lesion and cecum (M-mucosa; S-serosa), including BPC 157 (10 μg), NOS blocker L-NAME (5 mg), NOS substrate L-arginine (100 mg) alone or combined, and saline bath of equal volume (controls). Rats were then left after abdominal closure undisturbed until sacrifice, at day 1 or day 7. aP < 0.05 vs control.
- Citation: Drmic D, Samara M, Vidovic T, Malekinusic D, Antunovic M, Vrdoljak B, Ruzman J, Milkovic Perisa M, Horvat Pavlov K, Jeyakumar J, Seiwerth S, Sikiric P. Counteraction of perforated cecum lesions in rats: Effects of pentadecapeptide BPC 157, L-NAME and L-arginine. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(48): 5462-5476
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i48/5462.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i48.5462