Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2018; 24(45): 5131-5143
Published online Dec 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5131
Published online Dec 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5131
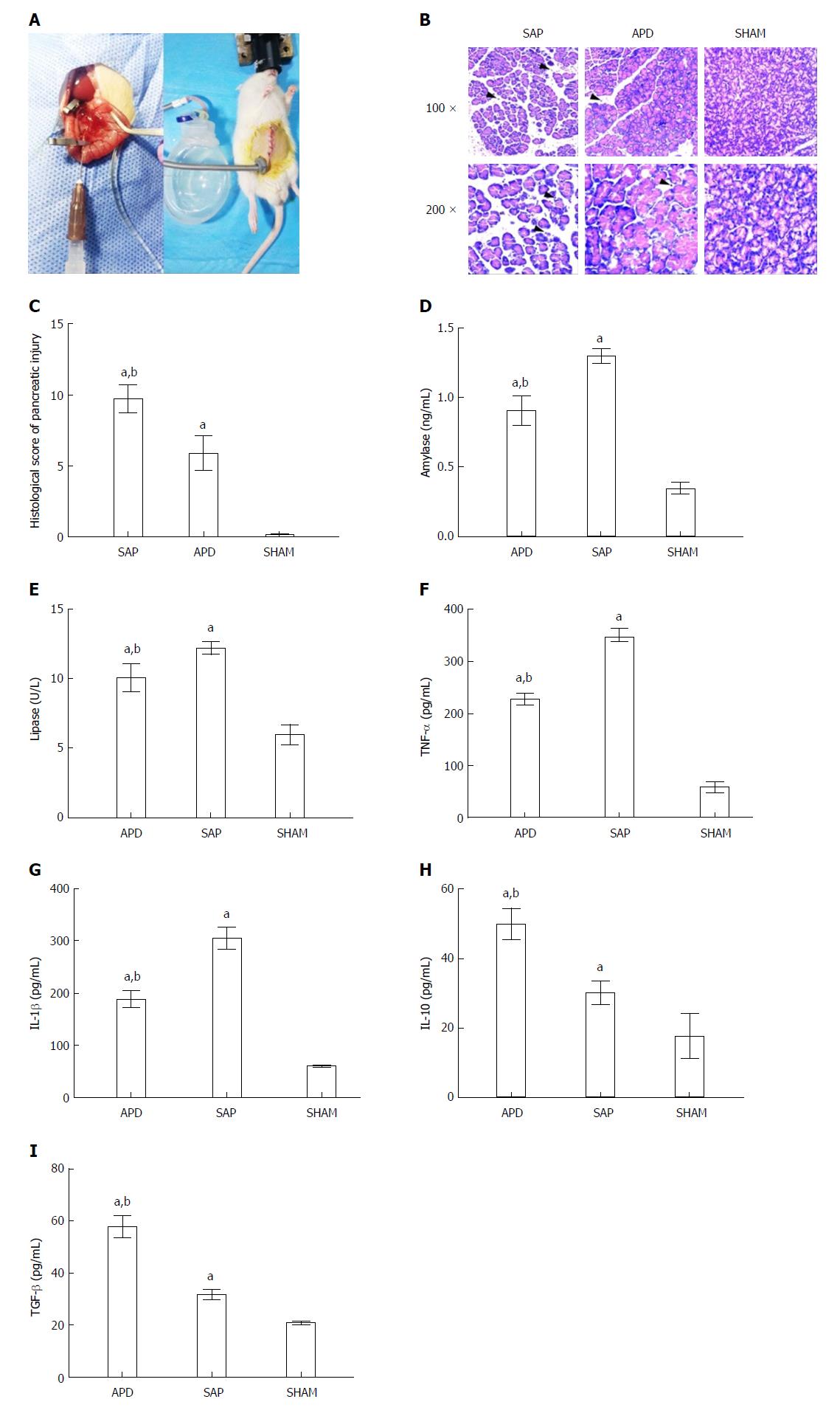
Figure 1 Abdominal paracentesis drainage ameliorates severe acute pancreatitis in a rat model.
A: Model establishment. Retrograde injection of Na-taurocholate (left) and a rat after abdominal paracentesis drainage (APD) treatment (right); B and C: Histopathological analysis of the pancreas. Comprehensive disruption of the pancreatic structure with widespread infiltration of leukocytes, acinar cell vacuolization and necrosis was observed in severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) rats; localized leukocyte infiltration and relatively intact acinar structure were observed in APD rats; D-I: Plasma levels of amylase, lipase, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-10 and transforming growth factor-β, respectively. Data indicate the mean ± SD of six mice (C-I). aP < 0.05 vs sham, bP < 0.05 vs SAP.
- Citation: Liu RH, Wen Y, Sun HY, Liu CY, Zhang YF, Yang Y, Huang QL, Tang JJ, Huang CC, Tang LJ. Abdominal paracentesis drainage ameliorates severe acute pancreatitis in rats by regulating the polarization of peritoneal macrophages. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(45): 5131-5143
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i45/5131.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5131