Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2018; 24(45): 5109-5119
Published online Dec 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5109
Published online Dec 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5109
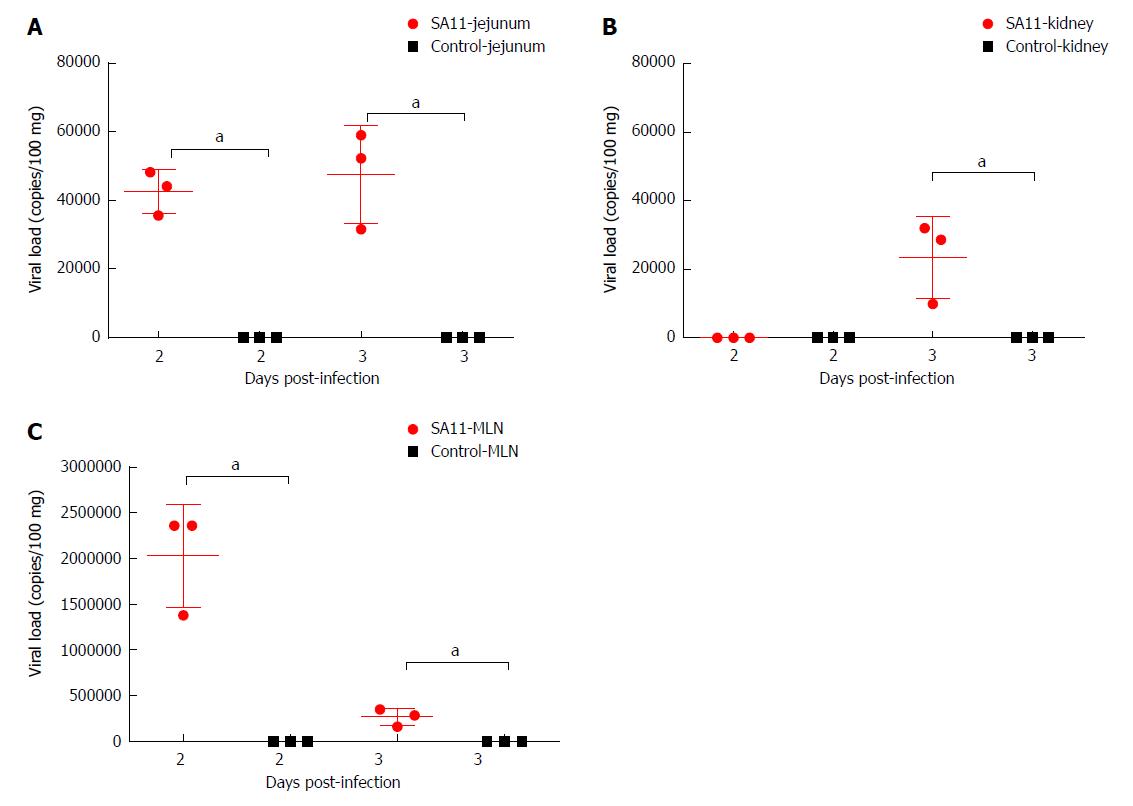
Figure 3 Comparison of viral load in different organs of neonatal rhesus monkeys inoculated with SA11 or medium without serum.
A: Viral load in the jejunum of neonatal rhesus monkeys inoculated with SA11 or medium without serum at 2 dpi and 3 dpi; B: Viral load in kidney of neonatal rhesus monkeys inoculated with SA11 or medium without serum at 2 dpi and 3 dpi; C: Viral load in the mesenteric lymph nodes of neonatal rhesus monkeys inoculated with SA11 or medium without serum at 2 dpi and 3 dpi. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD, n = 3, aP < 0.01.
- Citation: Yin N, Yang FM, Qiao HT, Zhou Y, Duan SQ, Lin XC, Wu JY, Xie YP, He ZL, Sun MS, Li HJ. Neonatal rhesus monkeys as an animal model for rotavirus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(45): 5109-5119
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i45/5109.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5109