Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2018; 24(45): 5095-5108
Published online Dec 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5095
Published online Dec 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5095
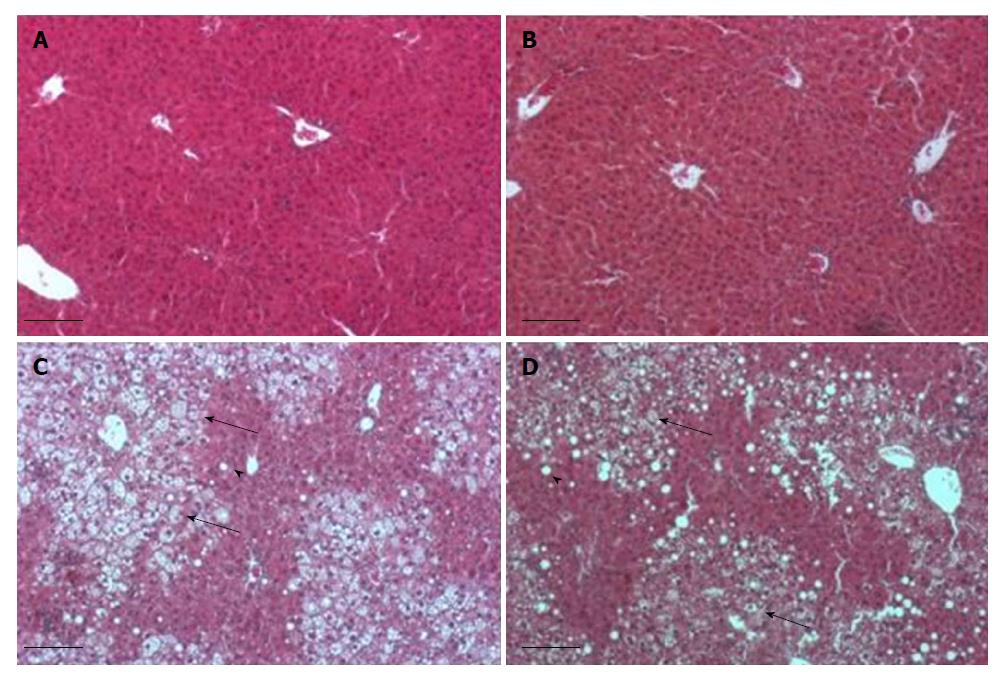
Figure 3 Histological sections stained by hematoxylin eosin of livers from mice fed regular diet and regular water (A), regular diet and electrolyzed alkaline water (B), high fat diet and regular water (C), high fat diet and electrolyzed alkaline water (D).
Note the prominent steatosis in mice fed on high-fat diet. Microvesicular inclusions (big arrow), macrovesicular inclusion (small arrow).
- Citation: Jackson K, Dressler N, Ben-Shushan RS, Meerson A, LeBaron TW, Tamir S. Effects of alkaline-electrolyzed and hydrogen-rich water, in a high-fat-diet nonalcoholic fatty liver disease mouse model. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(45): 5095-5108
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i45/5095.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5095