Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2018; 24(45): 5095-5108
Published online Dec 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5095
Published online Dec 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5095
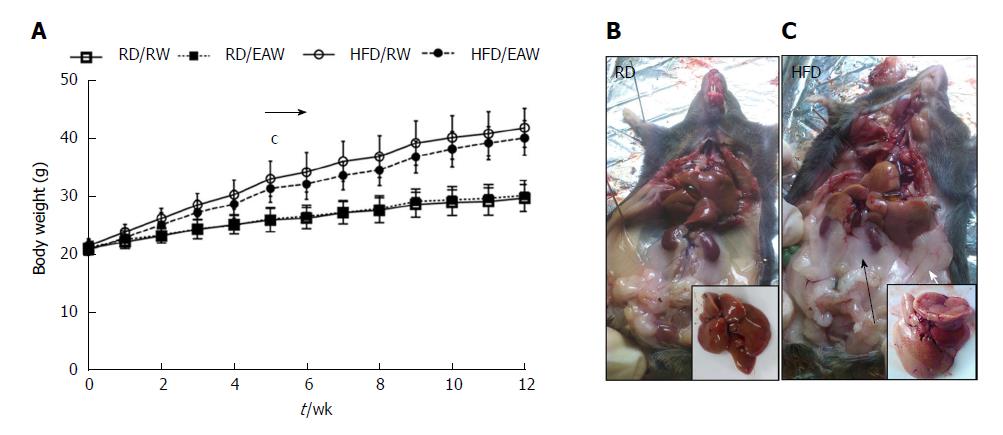
Figure 1 Effect of electrolyzed-alkaline water on body weight and composition.
A: Body weight (n = 12, mean ± SD) cshows significant diference between high-fat and regular diets. Mann Whitney and Kruskal-Wallis cP < 0.001); B and C: Ventral view of dissected mice after 12 wk of the experiment. Black arrow: Retroperitoneal fat pads; white arrow epididymal fat pad. Insert: Fresh dissected liver. RW: Regular water; EAW: Electrolysed alkaline water; RD: Regular diet; HFD: High fat diet.
- Citation: Jackson K, Dressler N, Ben-Shushan RS, Meerson A, LeBaron TW, Tamir S. Effects of alkaline-electrolyzed and hydrogen-rich water, in a high-fat-diet nonalcoholic fatty liver disease mouse model. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(45): 5095-5108
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i45/5095.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5095