Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2018; 24(44): 4989-5004
Published online Nov 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i44.4989
Published online Nov 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i44.4989
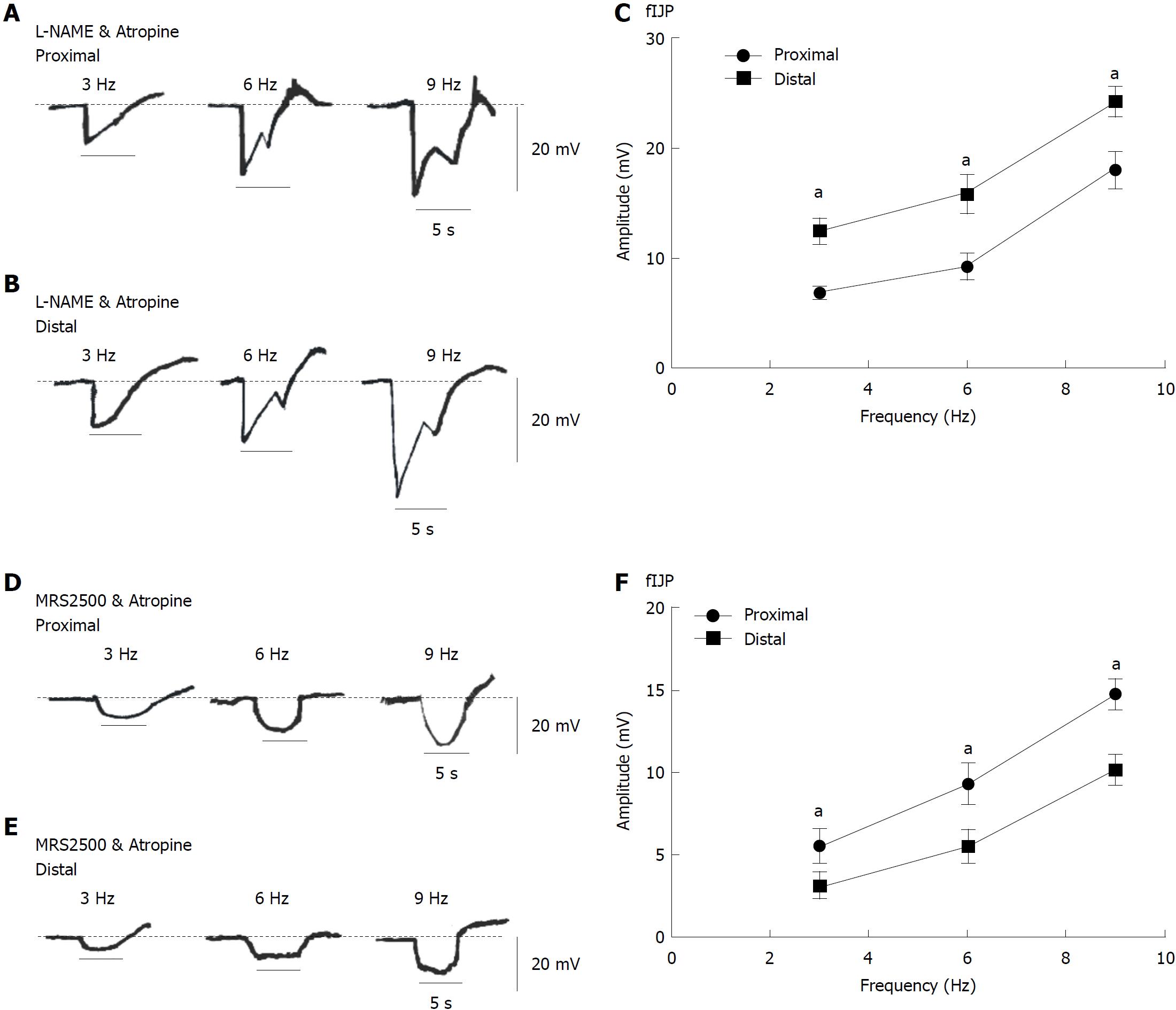
Figure 7 Fast inhibitory junction potential and slow inhibitory junction potential elicited by electrical field stimulation in smooth muscles of the proximal and distal colon.
A and B: Atropine and L-NAME treatment blocked excitatory junction potentials (EJPs) and decreased slow inhibitory junction potentials (sIJPs) but had no effect on fast IJPs (fIJPs) in colonic muscles from both ends. D and E: Atropine and MRS2500 treatment blocked EJPs and decreased fIJPs but had no effect on sIJPs in colonic muscles from both ends. C and F: Summary of data showing the average amplitude of fIJPs and sIJPs (in the presence of atropine and L-NAME, n = 8; in the presence of atropine and MRS2500, n = 7; aP < 0.05). fIJP: Fast inhibitory junction potential; sIJP: Slow inhibitory junction potential.
- Citation: Lu C, Huang X, Lu HL, Liu SH, Zang JY, Li YJ, Chen J, Xu WX. Different distributions of interstitial cells of Cajal and platelet-derived growth factor receptor-α positive cells in colonic smooth muscle cell/interstitial cell of Cajal/platelet-derived growth factor receptor-α positive cell syncytium in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(44): 4989-5004
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i44/4989.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i44.4989