Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2018; 24(41): 4652-4662
Published online Nov 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4652
Published online Nov 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4652
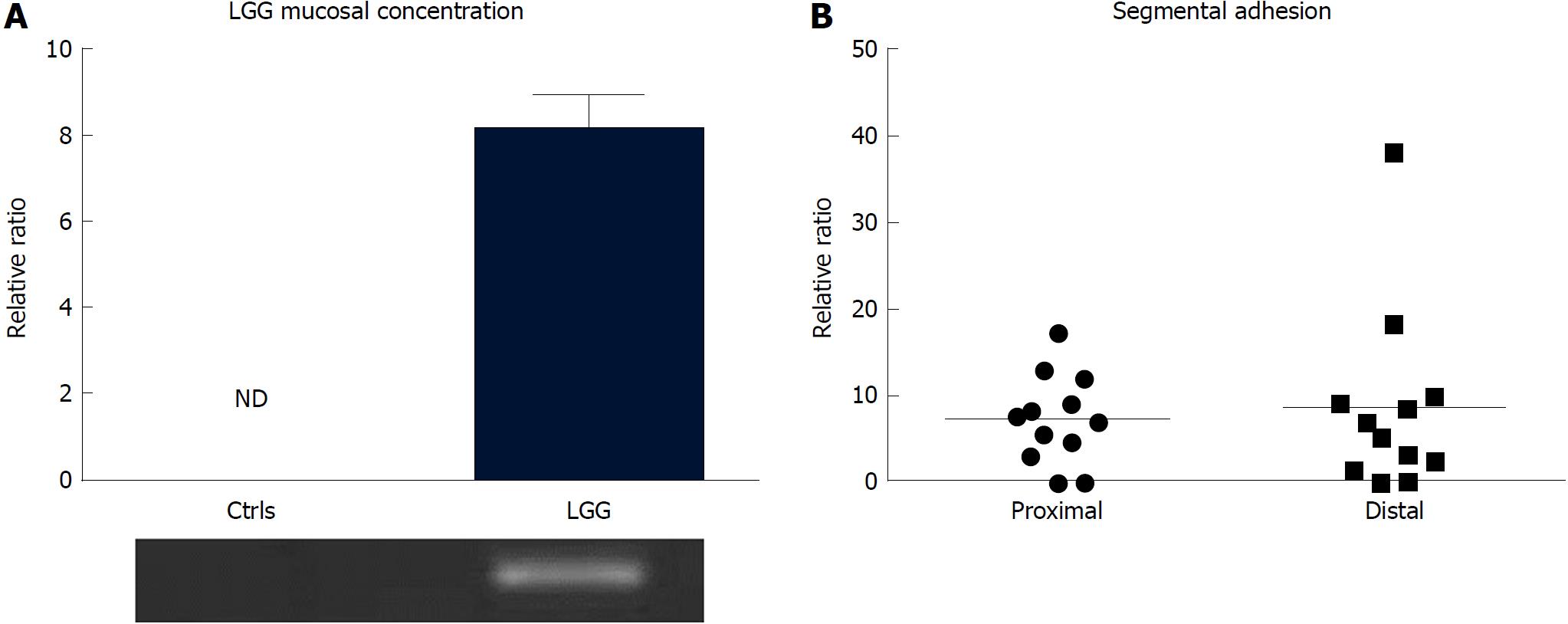
Figure 5 Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG adhesion in the normal colon in vivo after 7 d of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG administration.
A: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) detection in the colon of normal subjects who did (n = 12) and did not (n = 10) consume the probiotic formulation. Relative value bars and visualization on an agarose gel are shown. Mean ± standard error is represented; B: Relative segmental adhesion of LGG in the proximal and distal colon biopsies (n = 12 per group), with the bars representing the mean values. ND: Not detectable; LGG: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG.
- Citation: Pagnini C, Corleto VD, Martorelli M, Lanini C, D’Ambra G, Di Giulio E, Delle Fave G. Mucosal adhesion and anti-inflammatory effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in the human colonic mucosa: A proof-of-concept study. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(41): 4652-4662
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i41/4652.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4652