Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2018; 24(41): 4652-4662
Published online Nov 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4652
Published online Nov 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4652
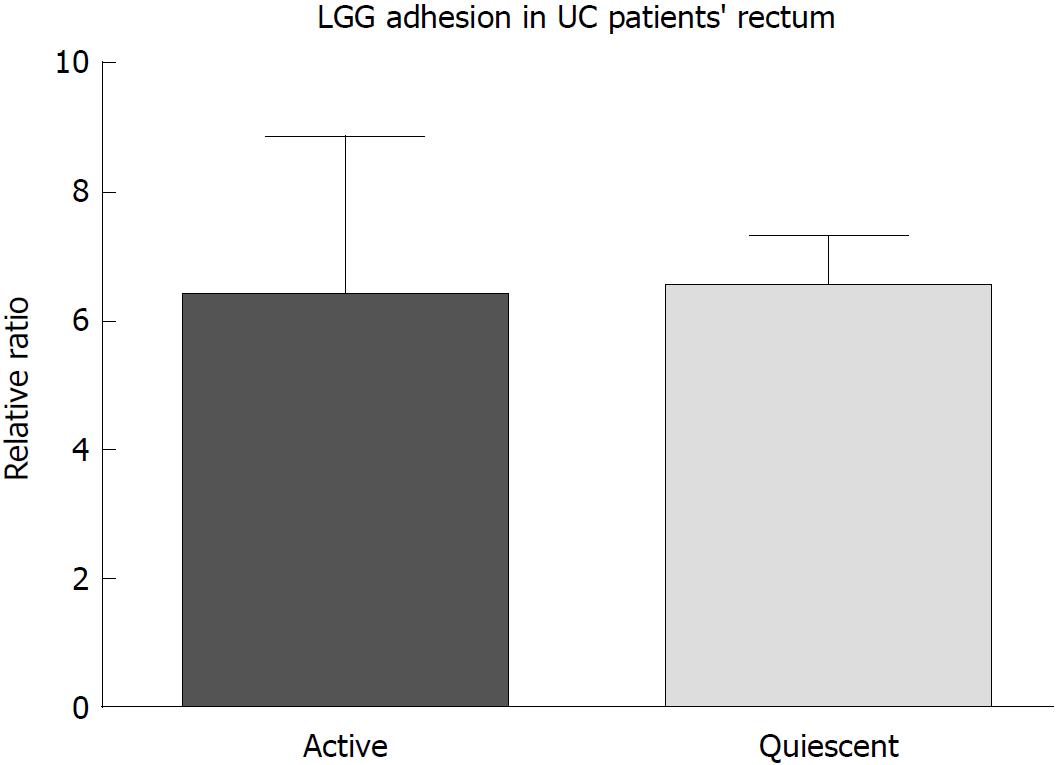
Figure 2 Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG adhesion in bioptic samples from the rectum of ulcerative colitis patients was evaluated by the ex vivo organ culture experimental model.
Similar concentrations of adherent Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG were found in the mucosa from ulcerative colitis patients without and with active endoscopic inflammation, as defined by Mayo Endoscopic Scores of ≤ 1 and 2, respectively (n = 15 per group). Mean ± standard error is represented. LGG: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG; UC: Ulcerative colitis.
- Citation: Pagnini C, Corleto VD, Martorelli M, Lanini C, D’Ambra G, Di Giulio E, Delle Fave G. Mucosal adhesion and anti-inflammatory effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in the human colonic mucosa: A proof-of-concept study. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(41): 4652-4662
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i41/4652.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4652