Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2018; 24(41): 4643-4651
Published online Nov 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4643
Published online Nov 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4643
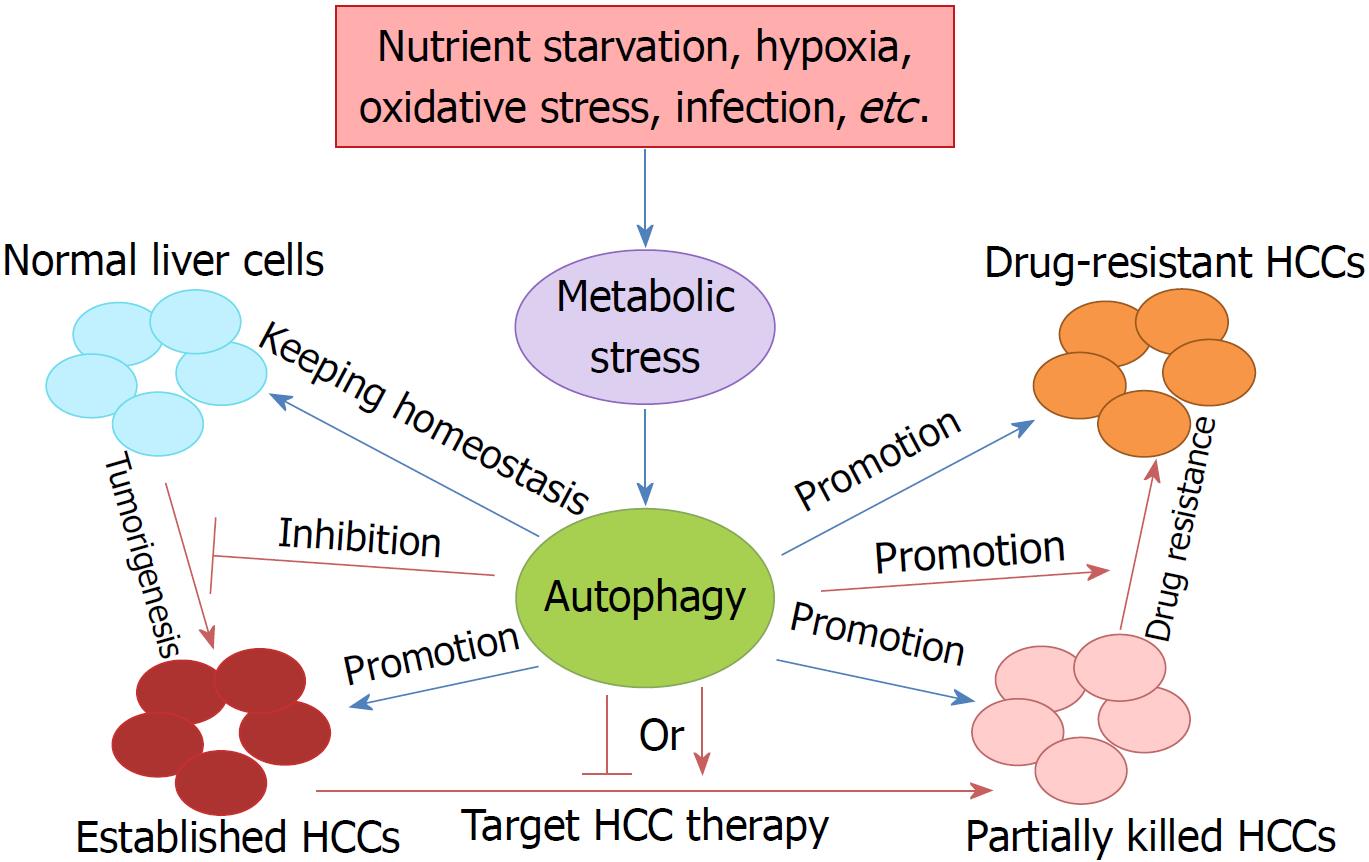
Figure 1 Different functions of autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Autophagy is significantly induced and improved through degrading macromolecules for de novo synthesis of biomolecules under the condition of metabolic stress, including nutrient starvation, hypoxia, oxidative stress, infection, etc. The function of autophagy in liver cancer is a topic of concern, and it plays multiple roles in different situations. In normal liver cells, basal autophagy has a housekeeping function, is involved in maintaining liver homeostasis, and preventing malignant tumorigenesis by removing harmful mitochondria and transformed liver cells. Once hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is established, autophagy plays a tumor promotion role in tumor development, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance. Thus, appropriate autophagy inhibition could effectively suppress HCC growth and metastasis. However, in target HCC therapy, the role of autophagy is uncertain, for either inhibition or promotion, according to the different characteristic of agents. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Huang F, Wang BR, Wang YG. Role of autophagy in tumorigenesis, metastasis, targeted therapy and drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(41): 4643-4651
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i41/4643.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4643