Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2018; 24(40): 4565-4577
Published online Oct 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i40.4565
Published online Oct 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i40.4565
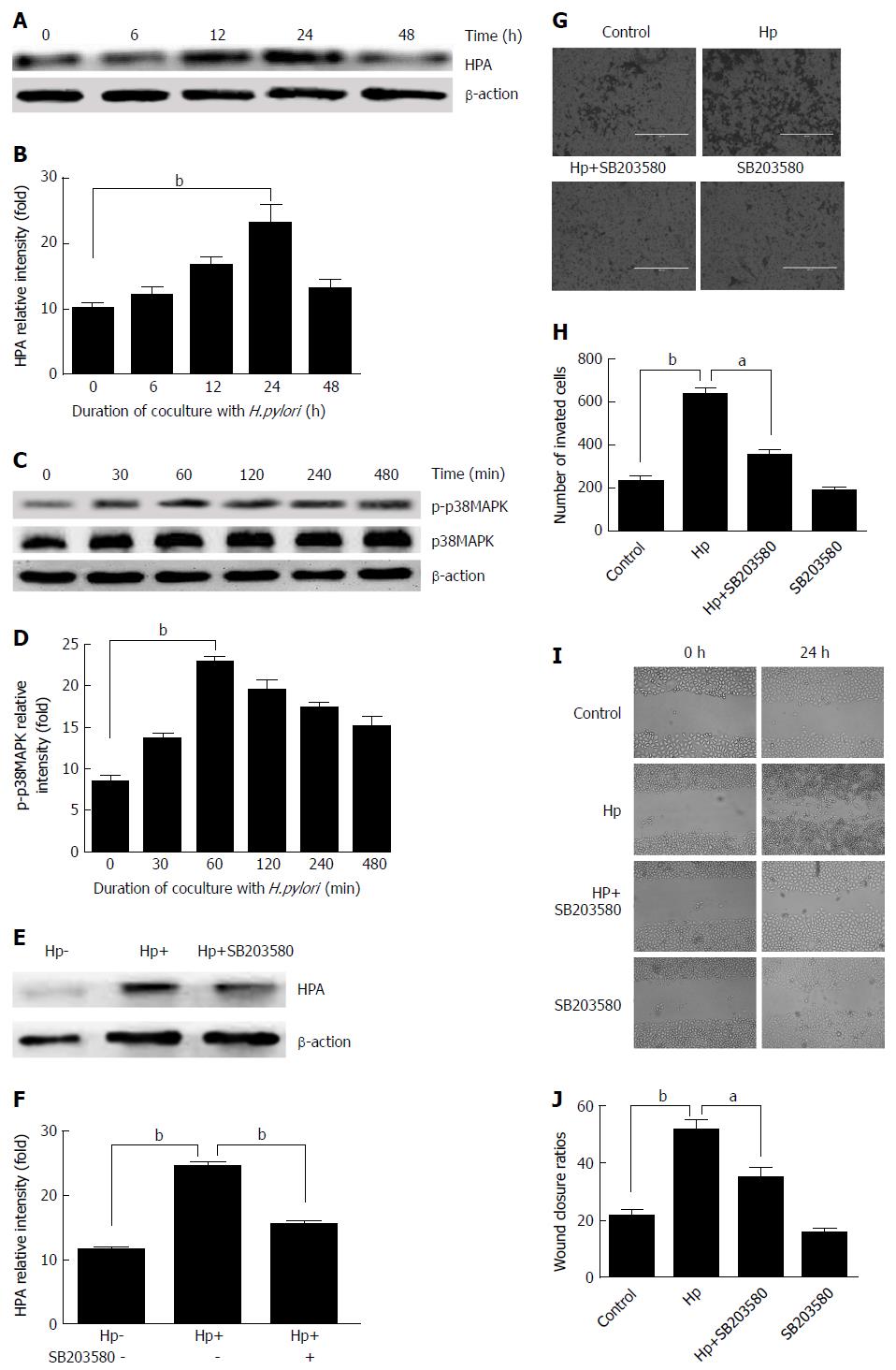
Figure 2 Heparanase protein expression following Helicobacter pylori infection in MKN-45 gastric cancer cells via the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.
A: Heparanase (HPA) expression was determined by Western blot at 0, 6, 12, 24, and 48 h after Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection; B: Quantitative Western blot results of HPA; C: p-p38MAPK expression was determined by Western blot at 0, 30, 60, 120, and 480 min after H. pylori infection; D: Quantitative Western blot results of p-p38MAPK; E: HPA expression when the MAPK inhibitor SB203580 was given to MKN-45 cells before H. pylori infection; F: Quantitative Western blot results of HPA when the MAPK inhibitor SB203580 was given. bP < 0.01 compared with the value at 0 h. G, H: Cell invasion rates in the three groups detected using a Transwell invasion assay. I, J: Migration rates in the three groups detected using a scratch migration assay. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. HPA: Heparanase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
- Citation: Liu LP, Sheng XP, Shuai TK, Zhao YX, Li B, Li YM. Helicobacter pylori promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by enhancing heparanase expression. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(40): 4565-4577
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i40/4565.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i40.4565