Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2018; 24(4): 537-542
Published online Jan 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i4.537
Published online Jan 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i4.537
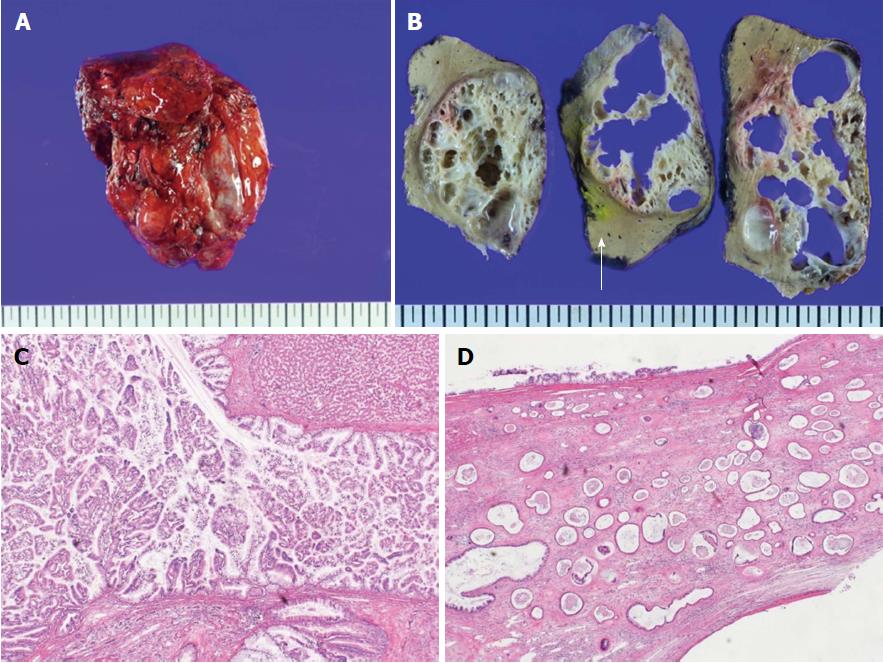
Figure 5 Histologic findings of intraductal papillary neoplasm of bile duct.
A: The resected hepatic mass was a multilocular cystic neoplasm with septation and a mural nodule; B: It had communication to segmental bile duct, although it was not connected to main bile duct (white arrow: Main bile duct); C: In the dilated bile duct, normal epithelial lining with abrupt papillary epithelial portions suggests IPNB. (HE, 100 ×); D: Multifocal stromal invasion multifocal stromal invasion with a tubulopapillary mucin component, suggestive of invasive adenocarcinoma with high-grade dyplasia. (HE, 40 ×). 300 mm × 225 mm (300 × 300 DPI).
- Citation: Lee JM, Lee JM, Hyun JJ, Choi HS, Kim ES, Keum B, Jeen YT, Chun HJ, Lee HS, Kim CD, Kim DS, Kim JY. Intraductal papillary bile duct adenocarcinoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumor in a case of neurofibromatosis type 1. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(4): 537-542
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i4/537.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i4.537