Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2018; 24(4): 511-518
Published online Jan 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i4.511
Published online Jan 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i4.511
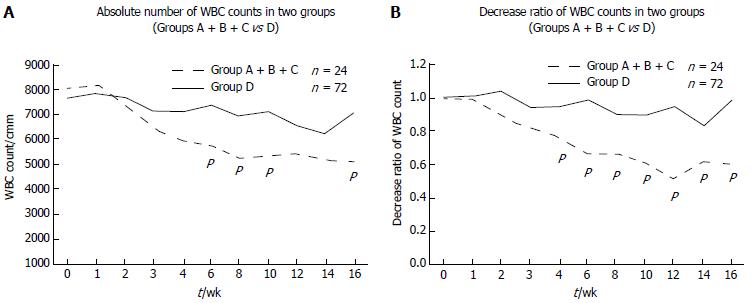
Figure 1 Change of white blood cell counts (Group A, B and C vs D).
A: Absolute number of WBC counts in two groups (Groups A, B and C vs D). WBC gradually decreased after the thiopurine was started in both the mutant (n = 24) and the wild type. The WBC count of the mutant was lower and statistically significant at 6, 8, 10 and 16 wk (P = 0.0271, 0.0037, 0.0051 and 0.0185, respectively); B: Decrease rate of the WBC counts in two groups (Groups A, B and C vs D). The decrease rate was higher in the variants (n = 24) than the wild (n = 72) and statistically significant at 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 and 16 wk (P = 0.004, 0.0001, 0.0012, 0.0022, 0.00001, 0.0264 and 0.0031, respectively). We set 1.0 as the WBC count at the beginning of thiopurines. WBC: White blood cell.
- Citation: Kojima Y, Hirotsu Y, Omata W, Sugimori M, Takaoka S, Ashizawa H, Nakagomi K, Yoshimura D, Hosoda K, Suzuki Y, Mochizuki H, Omata M. Influence of NUDT15 variants on hematological pictures of patients with inflammatory bowel disease treated with thiopurines. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(4): 511-518
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i4/511.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i4.511