Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2018; 24(4): 461-474
Published online Jan 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i4.461
Published online Jan 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i4.461
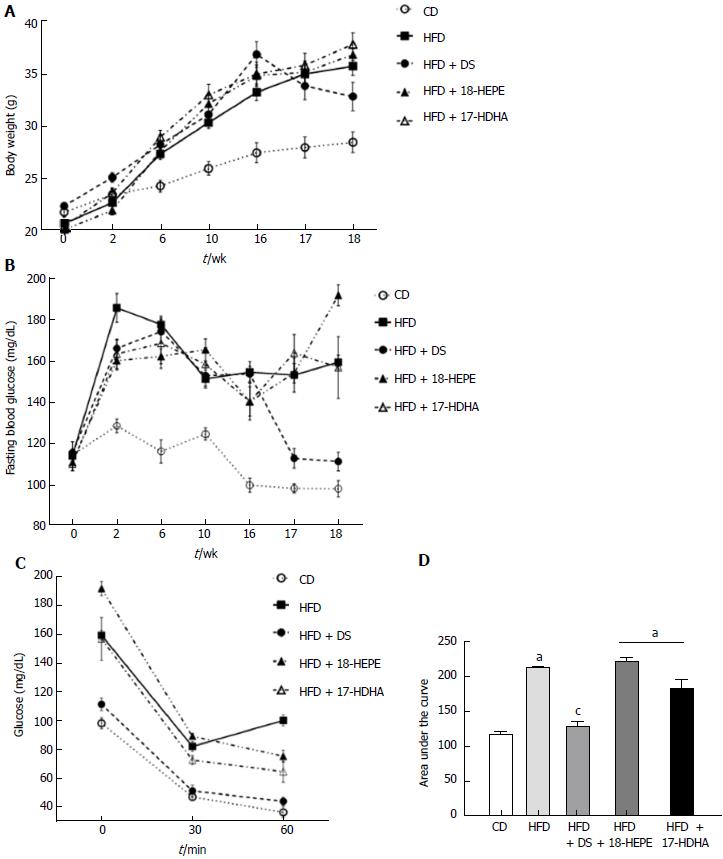
Figure 1 Weight, blood glucose and insulin tolerance test in an obesity/ nonalcoholic fatty liver disease model in C57BL/6 mice.
Weight (A), fasting glucose (B), Insulin tolerance test (C) and area under the curve from ITT data (D). All data are mean ± SEM. Groups: CD (n = 6), HFD (n = 6), HFD + DS (n = 6), HFD + 18-HEPE (n = 6), HFD + 17-HDHA (n = 6). aP < 0.05 vs CD, cP < 0.05 vs HFD by Mann-Whitney U test. HFD: High-fat, fructose-enriched diet.
- Citation: Rodriguez-Echevarria R, Macias-Barragan J, Parra-Vargas M, Davila-Rodriguez JR, Amezcua-Galvez E, Armendariz-Borunda J. Diet switch and omega-3 hydroxy-fatty acids display differential hepatoprotective effects in an obesity/nonalcoholic fatty liver disease model in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(4): 461-474
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i4/461.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i4.461