Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2018; 24(36): 4152-4163
Published online Sep 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i36.4152
Published online Sep 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i36.4152
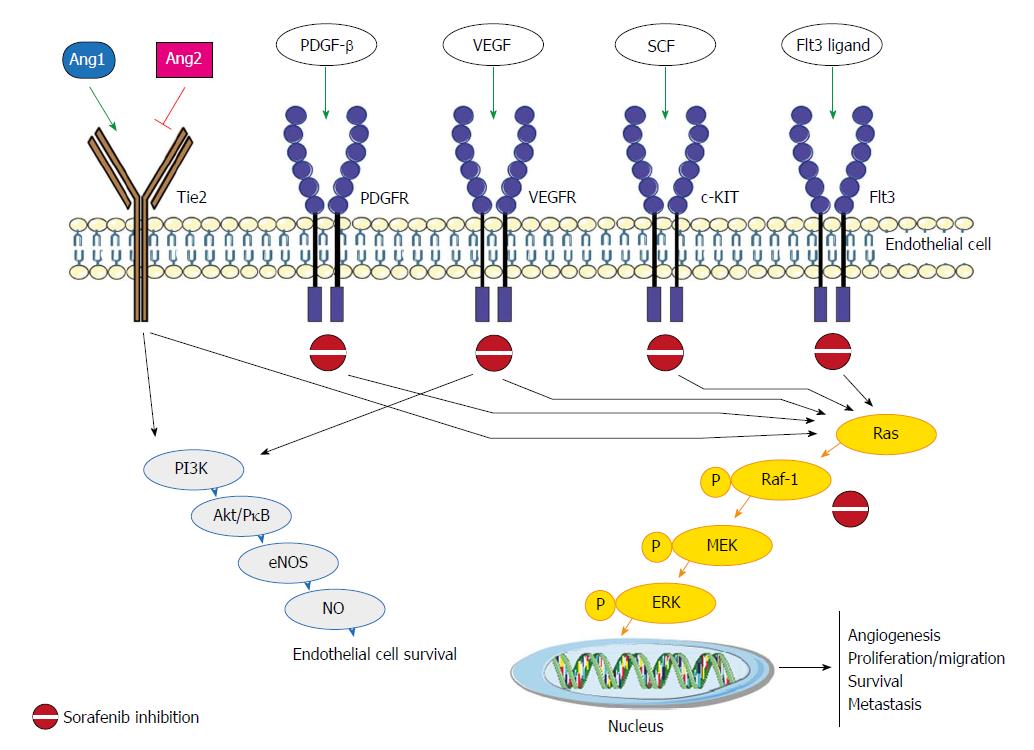
Figure 1 Sorafenib pathaway and the main molecular factors.
Ang: Angiopoietin; Tie2: Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor; PDGFR: Platelet-derived growth factor receptors; VEGFR: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; SCF: Stem cell factor; PI3K: PhosphatidylInositol 3-Kinase; Akt/PKB: Protein-chinasi B; eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; NO: Nitric oxide; P: Phospho-; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; ERK: Extracellular signal–regulated kinase.
- Citation: Marisi G, Cucchetti A, Ulivi P, Canale M, Cabibbo G, Solaini L, Foschi FG, De Matteis S, Ercolani G, Valgiusti M, Frassineti GL, Scartozzi M, Casadei Gardini A. Ten years of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma: Are there any predictive and/or prognostic markers? World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(36): 4152-4163
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i36/4152.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i36.4152