Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2018; 24(34): 3861-3870
Published online Sep 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i34.3861
Published online Sep 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i34.3861
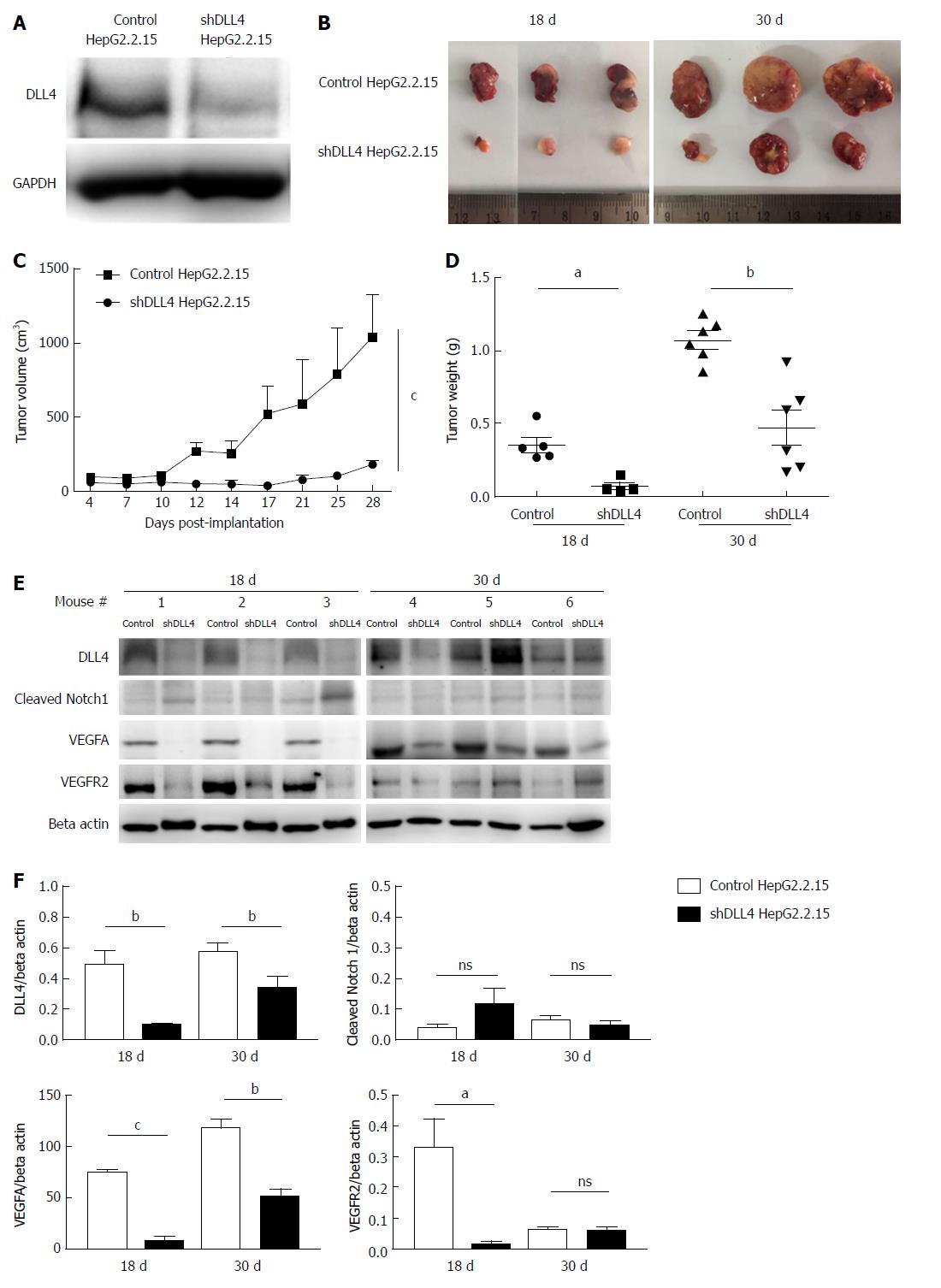
Figure 1 Delta-like ligand 4 expression promotes hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma tumour growth in vivo.
A: Western blot analyses of DLL4 expression in HepG2.2.15 stably transfected with shDLL4 or control vector. GAPDH was used as the loading control. B-D: HepG2.2.15 transfected with shDLL4 or control vector were subcutaneously injected into athymic nude mice (B) (1 × 107 cells per mouse, n = 4-6). Tumour volume (C) and tumour weights (D) are shown. At 18 d and 30 d after implantation, tumours were collected and analysed for DLL4, cleaved Notch1, VEGFA, and VEGFR2 by western blot. Beta-actin was used for the loading control. The blots cropped from different parts of the same gel (E). Band intensities from (E) were measured and the results are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (F). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001.
- Citation: Kunanopparat A, Issara-Amphorn J, Leelahavanichkul A, Sanpavat A, Patumraj S, Tangkijvanich P, Palaga T, Hirankarn N. Delta-like ligand 4 in hepatocellular carcinoma intrinsically promotes tumour growth and suppresses hepatitis B virus replication. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(34): 3861-3870
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i34/3861.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i34.3861