Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2018; 24(34): 3834-3848
Published online Sep 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i34.3834
Published online Sep 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i34.3834
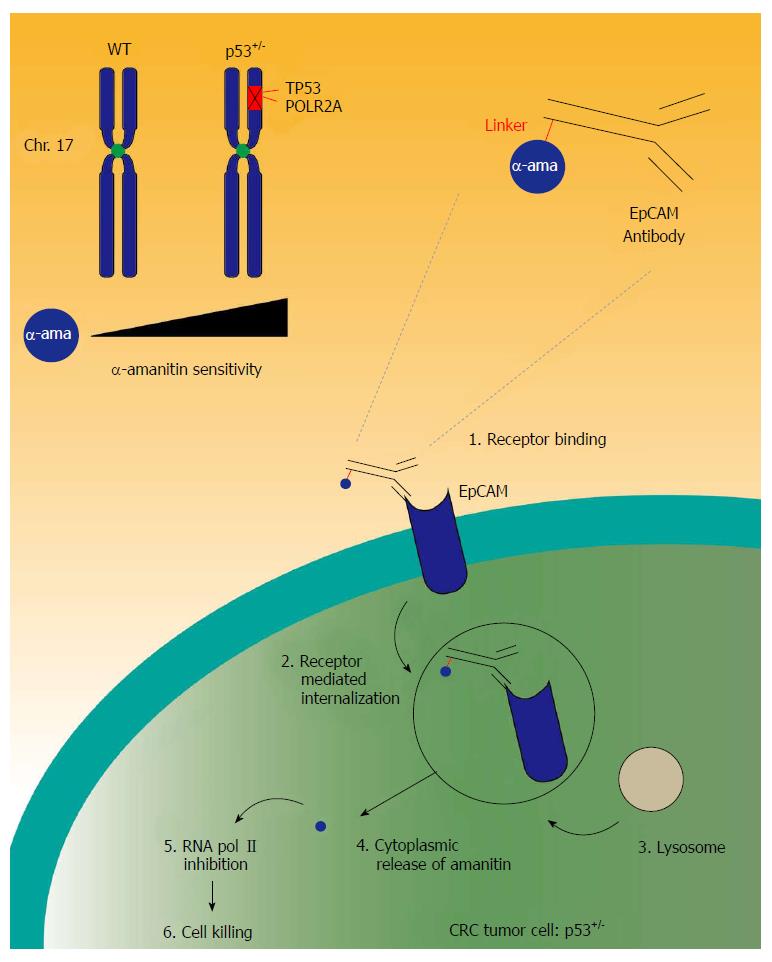
Figure 2 Working model of α-amanitin antibody-drug conjugates.
Genomic deletion of p53 frequently encompasses neighboring essential genes such as POLR2A. Colorectal cancer (CRC) cells displaying this loss are vulnerable to α-amanitin. The figure summarizes the different steps in α-amanitin-based antibody drug conjugate (ADC) killing of CRC cells with hemizygous p53 loss. (1) The ADC binds to CRC cells expressing epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM). (2) Hereafter, the ADC is internalized via receptor-mediated endocytosis. After fusing with lysozyme (3) the α-amanitin is released in the cytoplasm (4), leading to inhibition of the catalytic subunit of RNA polymerase II complex (5). Suppression of POLR2A will ultimately lead to cell death (6).
- Citation: Van der Jeught K, Xu HC, Li YJ, Lu XB, Ji G. Drug resistance and new therapies in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(34): 3834-3848
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i34/3834.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i34.3834